Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 7
The Correlation between Uromodulin and Renal Function in Preeclamptic Women with Preterm Birth
Alaa Saadi Abbood1*, Suaad A Brakhas2 and Sahar AH AL-Sharqi1
*Correspondence: Alaa Saadi Abbood, Department of Biology, College of Science, Mustansiriyah University, Iraq, Email:
Abstract
Preeclampsia is a major determinant of fetal and maternal morbidity and mortality and is a systemic disorder of pregnancy characterized by various manifestations of organ dysfunction, chief among them hypertension and proteinuria. Samples were collected from 25 preeclamptic women with preterm and 20 normotensive women in the third trimester of pregnancy (>27 weeks) with an age range of 19-46 years for preeclamptic patients compared to 20-41 years for control subjects. Measurements showed great difference with high statistical significance. Preeclamptic patients had significantly higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure measurements , Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) Mean ± Standard deviation 153.2 ± 11.4 the mean of preeclamptic women and 122 ± 4.2 for normotensive and Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) Mean ± Standard deviation 91.6 ± 9.0.4the mean of preeclamptic women and 79 ± 3.2for normotensive . There was great statistical discrepancy in renal function tests between the two studied groups. Preeclamptic patients had significantly higher levels of all three renal function tests. Some had blood urea and serum Creatinine levels above normal limits, Blood urea Mean ± Standard deviation52.9 ± 6.6 while normotensive is 28.1 ± 6.5, the Serum Creatinine Mean ± Standard deviation 1.8 ± 0.28 while normotensive is 0.7 ± 0.14 and the Serum uric acid Mean ± Standard deviation 7.6 ± 0.78 while normotensive is 3.9 ± 0.91. The present study show significantly decreased p<0.05) in level of Uromodulin in the serum of preeclamptic women with preterm theMean ± Standard deviation 15.8 ± 5.2 for preeclamptic women while the normotensive Mean ± Standard deviation is 19.9 ± 1.5, and In preeclamptic patients, correlation studies of uromodulin withB. urea had weak positive correlation the value is 0.223, and S. creatinine also had Weak +ve revealed directly relations the value is 0.258 and in Uric acid was Weak negative.
Keywords
Preeclampsia, Preterm, Uromodulin, Kidney function.
Introduction
Preeclampsia (PE) is defined as new-onset hypertension after 20 weeks of gestation that is associated with evidence of maternal organ or uteroplacental dysfunction, as well as proteinuria [1]. PE can rapidly deteriorate into a serious complication, which may include placental abruption, fetal growth restriction, stillbirth, or death of both mother and foetus [2]. The pathogenesis is multifactorial, with placental, vascular, renal, and immunological dysfunction all contributing [3]. Renal dysfunction is defined in PE as serum Creatinine levels exceeding 1.1 mg/dl or baseline Creatinine levels doubling. Renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate are frequently decreased in PE [4]. Calculating serum electrolytes, urea, and Creatinine concentrations may be a useful index for assessing physiological and pathological changes in PE [5] . Uric acid is the final product of the purine metabolism process in PE; elevated levels are a pre-symptomatic biomarker of kidney damage in women with PE and also a predictor of fetal death [6]. Under reasonable assumptions, serum uric acid measurement may be a useful test for predicting maternal complications [7]. Early preterm PE, in particular, was strongly associated with a variety of chronic renal disorders later in life [8]. Uromodulin is a major secretory protein produced by the cells lining the loop of Henle's thick ascending limb. Uromodulin is produced exclusively by cells lining the thick ascending limb (TAL), a tubular segment involved in the reabsorption of sodium chloride (NaCl), the handling of divalent cations (Ca2+ and Mg2+), and the regulation of urine concentration [9] Uromodulin is a glycoprotein attached to glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) that is recruited to the apical membrane, cleaved by a protease, and assembled in the urine into polymers that form a gellike structure [10]. The purpose of this study is to determine the relationship between uromodulin and renal function in preterm birth PE women.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology in Al- Elwiya and Al-Yarmouk teaching hospital during the period from December 2019 to June 2020. A questionnaire sheet was filled out for each woman in the study. The sample of this study is 20 normotensive women and 25 preeclamptic women with preterm. 5 ml of serum were collected immediately after delivery from women who delivered either vaginally or by caesarean section from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of hospitals. Human UMOD (Uromodulin) ELISA Kit from Al-Shkairate establishment for medical supply. also, Determination The concentration of serum Creatinine, uric acid, and urea were measured commercially by available kit ( spin react ) by kinetic method followed by Data analysis was performed using IBM(R) SPSS(R) Statistics software for Windows, version 26 (2019) and presented using Microsoft(R) Excel(R) (2016) MSO. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median (interquartile range, 25-75% IQR) when applicable. Statistical significance was set at P-value < 0.05 and , p< 0.001 with 95% confidence interval (CI).
Result
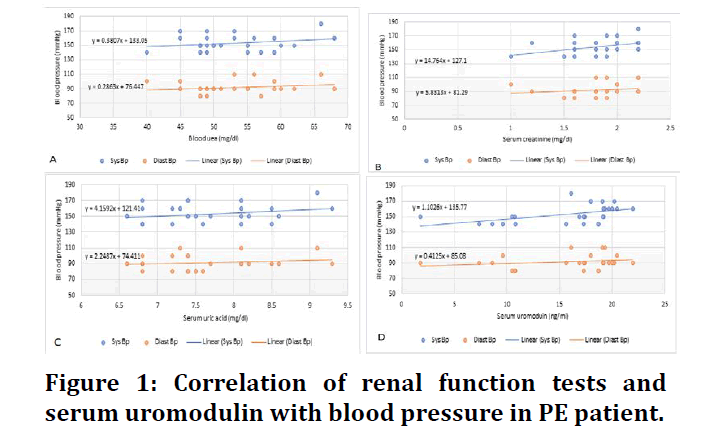
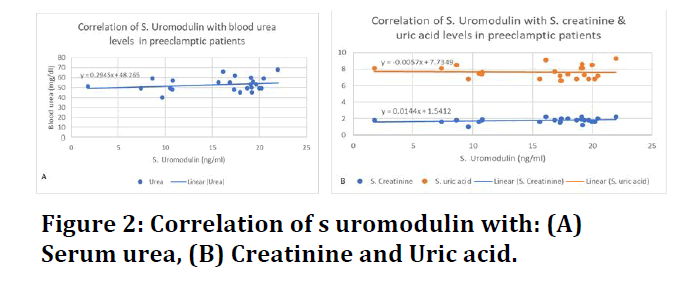
The present study included 25 PE women with preterm and 20 normotensive women (NT), the results show a great difference with high statistical significance. PE patients had significantly higher systolic the Mean ± SD was153.2 ± 11.4, while NT 122 ± 4.2 and diastolic blood pressure measurements 91.6 ± 9.0 in PE and 79 ± 3.2 in NTthe P<0.001, and the renal function tests of blood urea, Creatinine and uric acid serum were all normally distributed in both studied groups show in Table 1 and decreased in serum Uromodulin p< 0.05. In PE, correlation studies revealed varying degrees of directly proportional relation between renal function tests levels and blood pressure measurements the effect of serum Creatinine and uric acid appears to be greater on systolic blood pressure prediction than on diastolic pressure and directly proportional moderate relation of Uromodulin with systolic blood pressure measurements and a weak positive relation with diastolic measurements (Figure 1). PE patients had significantly higher levels of all three renal function tests. In PE patients, blood urea and serum Creatinine had weak positive correlation with uromodulin levels as shown in (Figure 2).
Table 1: Difference in renal function levels and Uromodulin (mg/dl) between PE patients and NT.
| Parameters test | PE | NT | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood urea (mg/dl) | 52.9 ± 6.6 | 28.1 ± 6.5 | 0.000 ** |
| Serum Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.8 ± 0.28 | 0.7 ± 0.14 | 0.000 ** |
| Serum uric acid (mg/dl) | 7.6 ± 0.78 | 3.9 ± 0.91 | 0.000 ** |
| Serum uromodulin (ng/ml) | 15.8 ± 5.2 | 19.9 ± 1.5 | 0.024* |
Data expressed as Mean ± Standard deviation ** High significant , p< 0.001 , , *significant , p< 0.05 PE: Preeclampsia, NT: Normotensive
Figure 1: Correlation of renal function tests and serum uromodulin with blood pressure in PE patient.
Figure 2: Correlation of s uromodulin with: (A) Serum urea, (B) Creatinine and Uric acid.
Discussion
The PE-related multi-systemic disorders in pregnancy that adversely affect mother and fetus health, with changes in renal function associated with preterm birth, in the 3rd trimester [11]. An increased rate of systolic and/diastolic uterine pressures seen in early pregnancy has also been shown to be predictive of premature birth [12].
In the present study the mean serum Creatinine showed a significant increase in PE pregnant women than in NT pregnant women. This increase in serum Creatinine may be due to the Renal tubular damage and reabsorption dysfunction which may be impaired markedly in PE causing an increased Creatinine and decrease in both renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate[13].With previous study they found increased concentrations of serum Creatinine in all PE pregnancies studied are similar with result reported by Them found that in most women with PE, the renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate were decreased as a consequence of increased afferent arteriolar resistance reduces the ultrafiltration coefficient [14].In the present study the blood urea level can be more increased in PE pregnant women than in NT pregnant women. This result is in good agreement with that reported by [15] who found that in PE both glomerular filtration rates and renal plasma flow decrease by 30% to 40% when compared with NT pregnancy.
Elevated serum uric acid levels increased the risk of PE. Serum uric acid levels are significantly higher in pregnant women with PE than in NT women. This is one of the most important indicators of PE [16]. In women with PE, maternal serum uric acid levels are a good predictor of fetal and neonatal outcomes [17]. Hyperuricemia is associated with oxidative stress and impaired renal function in PE as a result of placental ischemia and decreased maternal glomerular filtration rate [18]. The conclusion of [19] is that in healthy pregnancy, GFR is increased as early as the first trimester and the kidney continues to function at a higher rate throughout the gestation, whereas in hypertensive pregnancy, kidney function is decreased.
The current data demonstrate that serum uromodulin levels have decreased. Apart from genetic variations, uromodulin may regulate blood pressure under physiological conditions by interfering with tubular electrolyte and water transport, as evidenced by an inverse association between uromodulin and arterial hypertension in a large population-based study [20]. This finding supports the hypothesis that uromodulin is a resemblance to the avaso- and nephroprotective mediator molecule. Our findings corroborate previous clinical studies involving participants at high cardiovascular risk or with cirrhosis, in which a lower prevalence of arterial hypertension was observed in participants with increased serum or plasma uromodulin levels [21] found that s UMOD was inversely associated with arterial hypertension and the vasoconstrictive CtproEt- 1 prohormone, implying that Sumod has direct or indirect effects on blood pressure regulation. The current result confirms [22] that serum uromodulin behaves in the opposite direction of the various conventional renal retention markers, with decreasing concentrations associated with decreased kidney function. Reduced plasma uromodulin levels have been linked to worse clinical outcomes in chronic renal diseases, implying that plasma uromodulin may be a useful biomarker for predicting disease progression [23].
A more recent study [24] discovered that hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) are associated with an increased risk of maternal chronic kidney disease (CKD). The ratio of Creatinine to uromodulin was found to be significantly associated with kidney function, and maternal serum uric acid concentrations with urea, Creatinine are significantly increased beginning in early pregnancy and rapidly increased throughout pregnancy in women who develop PE [25].
Conclusion
The PE women with preterm had significantly higher levels of all three renal function tests, blood urea and serum Creatinine and uric acid levels above normal limits, and a low sUMOD levels were associated with preeclamptic women with preterm and might be considered as a risk factor for Pregnancy. The correlation studies with B. urea had weak positive correlation also S. Creatinine and Uric acid had Weak +ve directly revealed relations.
Acknowledgements
We gratitude to the Department of Biology, College of Science, Mustansiriyah University (http://uomustansiriyah.edu.iq/), Baghdad for advice and support.
References
- Fox R. Kitt J. Leeson P. et al. Preeclampsia risk factors, diagnosis, management and the cardiovascular impact on the offspring . J Clin Med 2019; 8:1625.
- Rana S, Lemoine E, Granger JP, Karumanchi SA. Preeclampsia: Pathophysiology, challenges, and perspectives. Circulation Res 2019; 124:1094-1112.
- Turbeville HR, Sasser JM. Preeclampsia beyond pregnancy: Long-term consequences for mother and child. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2020; 318:F1315-1326.
- Wilkerson R, Ogubodede A. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Emerg Med Clin North AM 2019; 37:301-316 .
- Charles N, Amarachukwu N, Ekpo E, et al. Changes in renal function among women with preeclampsia in a tertiary health institution in Nigeria. Int J Womens Health Reprod Sci 2020; 8:272-275.
- Essibn F, Itembe O, Foumane Pet al. Blood uric acid levels as marker of increased risk of preclampsia in serum preeclamptic patients. Health Sci Fis 2016; 17:7-11.
- Pecoraro V, Trenti T. Predictive value of serum uric acid levels foe adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes in pregnant women with high blood pressure. Eur J OBSt Gyne 2020; 252:447-454 .
- Kristensen JH, Basit S, Wohlfahrt J, et al. Pre-eclampsia and risk of later kidney disease: nationwide cohort study. BMJ 2019; 365:1516.
- Olden M, Corre T, Hayward C. Common variants in UMOD associate with urinary uromodulin levels: a meta-analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014; 25:1869–1882.
- Feig D. Meta-analysis suggests that metformin may reduce pre-eclampsia compared with insulin use during pregnancy. BMJ Evid Based Med 2019; 24:72-73.
- Jena MK, Sharma NR, Petitt M, et al. Pathogenesis of preeclampsia and therapeutic approaches targeting the placenta. Biomol 2020; 10:953.
- Stuart JJ, Tanz LJ, Cook NR, et al. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and 10-year cardiovascular risk prediction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018; 72:1252–1263.
- Göhner C, Plösch T, Faas MM. Immune-modulatory effects of syncytiotrophoblast extracellular vesicles in pregnancy and preeclampsia. Placenta 2017; 60:S41-51.
- Behrens I, Basit S, Melbye M, et al. Risk of post-pregnancy hypertension in women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: nationwide cohort study. BMJ 2018; 358:3078.
- Bellos I, Perigilaiotis V, Loutradis D, et al. The prognostic role of serum uric acid levels in preeclampsia. Clin J hypertension 2020; 22:826-834.
- Shakarami A, Masoumeh G, Fathi F. Association between maternal serum uric acid and preeclampsia. Arch Physiol Biochem J 2020; 126:1-4.
- Le TM, Nguyen LH, Phan NL, et al. Maternal serum uric acid concentration and pregnancy outcomes in women with preâ?eclampsia/eclampsia. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2019; 144:21-26.
- Einbinder Y, Biron-Shental T, Agassi-Zaitler M, et al. High-density lipoproteins (HDL) composition and function in preeclampsia. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2018; 298:405-413.
- Lopes van Balen VA, van Gansewinkel TA, de Haas S, et al. Maternal kidney function during pregnancy: Systematic review and metaâ?analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2019; 54:297-307.
- Tomimatsu T, Mimura K, Endo M, et al. Pathophysiology of preeclampsia: An angiogenic imbalance and long-lasting systemic vascular dysfunction. Hypertens Res 2017; 40:305-310.
- Then C, Thorand B, Then HL, et al. Serum uromodulin is inversely associated with arterial hypertension and the vasoconstrictive prohormone CT-proET-1 in the population-based KORA F4 study. Plos one 2020; 15:e0237364.
- Risch L, Lhotta K, Meier D, et al. The serum uromodulin level is associated with kidney function. Clin Chem Lab Med 2014; 52:1755-1761.
- Tan F, Zeng Y, Yan L, et al. Low plasma uromodulin is a predictor of early stage chronic kidney disease progression. Int J Clin Exp Med 2017; 10:8055-8059.
- Barrett P, Mccarthy F, Evans M, et al. Hypertension disorders of pregnancy and the nrisk of chronic kidney disease .PLOS medicin J 2020; 17:el003255.
- Singh AK, Kumar R, Singh VK, et al. Serum uric acid levels in pregnancy induced hypertension preeclampsia. Int J Clin Biochem Res 2018; 5:365-368.
Author Info
Alaa Saadi Abbood1*, Suaad A Brakhas2 and Sahar AH AL-Sharqi1
1Department of Biology, College of Science, Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, Iraq2Department of Immunology/Allergy Specialized Center, Baghdad, Iraq
Citation: Alaa Saadi Abbood, Suaad A Brakhas, Sahar AH AL-Sharqi,The Correlation between Uromodulin and Renal Function in Preeclamptic Women with Preterm Birth, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(7): 113-116
Received: 05-Jun-2021 Accepted: 08-Jul-2021