Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 7
Serum Calcium and Vitamin D Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
*Correspondence: Kanchana R, Department of Physiology, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, India, Email:
Abstract
Individuals with T2DM do not experience this increase in b-cell mass, in fact there is a significant decrease in b¬ cell mass. In addition to a decrease in b-cell mass, there is a 41% decrease (p<0.05) in relative b-cell volume. Individuals with T2DM when compared to their lean non diabetic counterparts, which can be partially explained by the increase in b-cell apoptosis that is also observed in individuals with T2DM. Finding suggests that b-cell apoptosis may be more pronounced in individuals with T2DM partly due to an increase in caspase-3 activity, and that it may contribute to the decrease in b-cell mass observed in this study- . The targeting of beta cell function early in the pathogenesis of T2DM is considered a critical intervention for the prevention of the diseases. It was also observed that the T2DM individuals with a vitamin D insufficiency showed a poor glycaemic control.
Keywords
Glycemia, B cells, Apoptosis.Introduction
Pathogenesis of T2DM diabetes is involves the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. People with T2DM are reported to have many abnormalities. Hence there is a necessity to identify modifiable risk factors. Evidences from the previous studies say that calcium and vitamin D are such factors, when modified may control the diseases. Hence this study was done to estimate the serum calcium and vitamin D levels in T2DM and compare the values with non-diabetic samples [1-5].
Methodology
5ml of blood was collected from patients with T2DM Plasma glucose levels was estimated by GOD-POD method (glucose oxidase -peroxidase method).Vit D levels were estimated by ELIZA method. Serum calcium was determined by Arsenazo method. Serum calcium was determined by Arsenazo method with the case controls.Results
Figure 1 shows the HbAl c, Plasma blood glucose levels, serum calcium, and vitamin D values among Diabetics and Non Diabetics. A p value of <0.01 was considered to be highly significant and was obtained for all parameters. A negative trend was seen between HbAlc and serum calcium in non-diabetics and between plasma blood glucose levels and vitamin D in non-diabetics. A positive trend was seen between plasma blood glucose levels and serum calcium in non-diabetics and also between vitamin D and serum calcium in none. From the results it was confirmed that a negative correlation was seen between plasma blood glucose levels and vitamin D in diabetics.
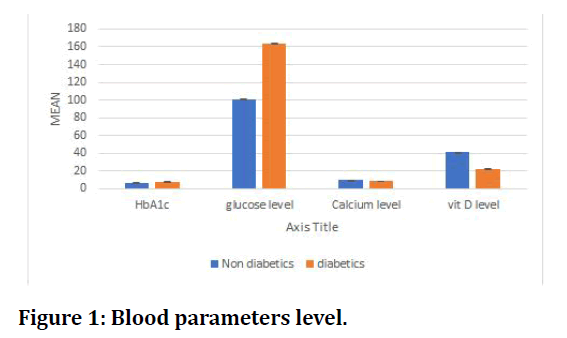
Figure 1: Blood parameters level.
Discussion and Conclusion
A negative correlation was seen between serum calcium, vitamin D levels and plasma blood glucose levels. A mcrease in plasma blood glucose levels was associated with decrease in serum calcium and vitamin D levels. Various studies had proved that vitamin D deficiency impairs the glucose mediated insulin secretion in our body. But the condition is restored when its supplemented. In this study A negative correlation was seen among serum calcium, vitamin D levels and HbA1c that is low serum calcium and vitamin D levels was associated with higher HbA1c [6-10].
Hence it was concluded from the study that supplementation of calcium along with vitamin D can prove to be a very cost effective and effective measure to control blood glucose levels in diabetics along with other measures such as exercise and oral hypoglycaemic.
References
- Christakos S, Barletta F, Buening M, et al. Vitamin D target proteins: Function and regulation. J Cell Biochem 2003; 88:238-44.
- Mathieu C, Gysemans C, Giulietti A, et al. Vitamin D and diabetes. Diabetologia 2005; 48:1247-57.
- Kolb H, Mandrup-Poulsen T. An immune ong1n of type 2 diabetes? Diabetologia 2005; 48:1038-50.
- Levy J, Gavin JR, Sowers JR. Diabetes mellitus: A disease of abnormal cellular calcium metabolism? Am J Med 1999; 96:260-73.
- Schleithoff SS, Zittermann A, Tenderich G, et al. Vitamin D supplementation improves cytokine profiles in patients with congestive heart failure: a double-blind, randomized, placebo- controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2006; 83:754-9.
- Bland R, Markovic D, Hills CE, et al. Expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxy lase in pancreatic islets. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2004; 89-90:121-5.
- Zeitz U, Weber K, Wolf E, et al. Impaired insulin secretory capacity in mice lacking a functional vitamin D receptor. FASEB J 2003; 17:509-11.
- Sooy K, Schermerhorn T, Noda M, et al. Calbindin-D(28k) controls (Ca(2))(i) and insulin release. Evidence obtained from calbindin-D(28k) knockout mice and beta cell lines. J Biol Chem 1999; 274:34343-9.
- Johnson JA, Grande JP, Roche PC, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of the 1,25 (OH) 2D3 receptor and calbindin D 28K in human and rat pancreas. Am J Physiol 1994; 267:e356-e360.
- Mathieu C, Gysemans C, Giulietti A, et al. Vitamin D and diabetes. Diabetologia 2006; 49:217-18.
Author Info
Department of Physiology, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, IndiaCitation: Kanchana R, Serum Calcium and Vitamin D Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(7): 451-452
Received: 07-Jul-2021 Accepted: 26-Jul-2021
