Review Article - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 5
Role of Forensic Odontology in the Identification of Victims of Mass Disaster: A Systematic Review
*Correspondence: Mahesh Shenoy, Department of Oral Diagnostic Sciences, Riyadh Elm University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, Email:
Abstract
Background: One of the important parts of management of mass disasters is the reorganization of the remains found after death of human beings. This procedure is usually carried out by forensic experts. It is very tough job because most parts of the body get damaged in massive destruction and it becomes difficult to identify the victim. There have been many methods which rely on the sufficient quantity of remains of the body for proper identification. Nowadays forensic dentistry is also being considered for the identification of the victims in mass disasters. This systematic review was carried out to assess the role of forensic odontology in the mass disasters.
Methods: There was extensive literature search in reliable and authentic databases like Pubmed, Scopus, Web of Sciences, Ovidsp for obtaining papers focussing on forensics sciences, forensic odontology, mass disasters, identification of victims since 1980 till 2021. Data were obtained concerning the following parameters: type of study, nature of study, mass disaster, subtype of mass disaster i.e. natural, criminal or accidental, country where the mass disaster took place, year of incidence of mass disaster, state where the disaster took place, enumeration of total number of victims in the mass disaster, percentage of the victims who got identified, percentage of affected human victims identified with forensic odontology alone, percentage of affected human beings identified on using forensic odontology in association with other forensic methods of identification.
Results: Total numbers of victims assessed in all the studies included in this systematic review were 22345. Among them (86.21%) victims were recognized. The percentages of victims identified by using forensic odontology alone were (15.21%). On the other hand (6.21%) victims were recognized with the help of forensic odontology along with other forensic methods. When there was analysis of other methods for reorganization of the victims in mass disasters then it was found that maximum number of victims were identified by personal visual reorganization (69.21%) followed by fingerprint (7.21%) and DNA (5.4%).
Conclusion: It can be concluded from this systematic review that forensic odontology can be used as an adjuvant in identification of victims of mass disasters. However more research will be required to establish forensic odontology as the golden standard for reorganization of victims in mass disasters.
Keywords
Forensic odontology, Mass disasters, Systematic reviewIntroduction
Death of human being is the biggest truth on this earth. There are several reasons for death of human beings. One of the important reasons for deaths and physical inability of human beings are the mass disasters. These are the conditions in which large number of human beings are killed or seriously injured at the same time and same place. These conditions of mass destructions are indiscriminate, violent and unexpected in nature. These conditions are termed as MDs (Mass Disasters). Since these conditions are very destructive therefore there is need for extensive management program to handle these conditions [1,2].
These conditions of massive destruction are usually categorised in three categories: criminal, accidental, and natural. The agency authorized to study the epidemiology and carry research on the disasters have described disaster. It has been described as a condition which completely destroys a region in such a manner that help is required from the external international as well as national sources. Besides disaster is also described as condition which is unexpected and sudden in onset causing severe destruction, damage and deaths of human beings. There have been some criteria which decide whether a condition is to be considered as disaster or not.
If any one of these criteria’s are fulfilled then a condition is termed as disaster and then it is transferred in the existing database as a disaster. These conditions are as follows [3,4].
• Killing of ten or more than ten people.
• The condition affecting hundred or more than hundred people at the same time and same place.
• Emergency has been declared in that area.
• Assistance from the international sources has been sought from that region.
Another means of classification of disasters is categorizing the disasters as closed disasters, open disasters and open disasters. Examples of open disasters are train accidents, tsunamis and earthquakes. In open massive disasters it has been found that names of the affected human beings are normally not known [5]. Examples of closed disasters include those conditions where names of the involved human beings are usually known. Some of these conditions include massive fires in the hotels, disasters involving ships and crashes of aeroplanes. Nowadays the prevalence of massive disasters have increased due to increase in the facilities for public travelling, increase in the incidence of natural calamity and increase in terrorism [6].
One of the important parts of management of such massive disasters is the reorganization of the remains found after death of human beings. This procedure is usually carried out by forensic experts. It is very tough job because most parts of the body get damaged in massive destruction and it becomes difficult to identify the victim. There have been many methods which rely on the sufficient quantity of remains of the body for proper identification. Nowadays forensic dentistry is also being considered for the identification of the victims in mass disasters [7,8]. Forensic odontology is based on the information obtained from the teeth and Para-oral structures. A major advantage of the forensic odontology is that the teeth of victims are not usually destroyed as compared to other parts of the body [9,10]. Therefore role of forensic odontology in mass disasters should be evaluated. Hence this systematic review was carried out to assess the role of forensic odontology in the mass disasters.
Materials and Methods
Inclusion criteria
Those published papers were selected which fulfilled following criterion:
• Papers which reflected application of forensic odontology in identification of victims in mass disasters.
• Papers which included other methods of forensic identification along with forensic odontology in management of mass disasters.
• Papers which were published in English language only.
Exclusion criteria
Those papers were not selected which were having following features:
Papers not discussing about the methods for identification of victims in mass disasters.
• Those literatures published in formats which were non-commercial in nature like abstract of conference.
• Papers published in language other than English
Data extracted
In this systemic review data were obtained concerning the following parameters: type of study, nature of study, mass disaster, subtype of mass disaster i.e. natural, criminal or accidental, country where the mass disaster took place, year of incidence of mass disaster, state where the disaster took place, enumeration of total number of victims in the mass disaster, percentage of the victims who got identified, percentage of affected human victims identified with forensic odontology alone, percentage of affected human beings identified on using forensic odontology in association with other forensic methods of identification, details of other forensic methods used for reorganization of victims of the mass disasters (Table 1).
Statistical analysis
IBM SPSS version and fourteenth version of Microsoft Excel was used for carrying out systemic review analysis. Analysis of percentage of the victims who got identified, percentage of affected human victims identified with forensic odontology alone, percentage of affected human beings identified on using forensic odontology in association with other forensic methods of identification among the groups was carried out with the help of independent sample t-tests. Differences among the means of groups were represented with t-test confidence intervals while difference among the population was represented by chi squared confidence intervals (95% CI) (Figure 1).
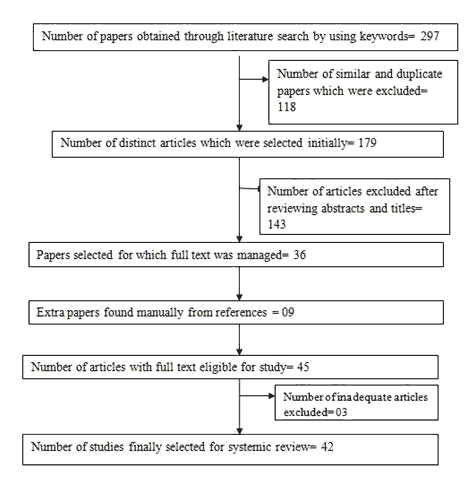
Figure 1: Flow chart representing the search of articles in this systematic review.
Table 1: Vital features of some of the studies included in this systematic review.
| Details of authors | Subtype of disaster | Type of disaster | Year of publication | Name of state or city affected | Name of country affected | Percentage of the victims recognized | Enumeration of total number of victims | Number of victims in which forensic odontology was used in association with other methods | Percentage of the victims recognized by forensic odontology alone | Details of the other methods used in the reorganization of |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bastiaan and associates | Bushfires | Natural | 1984 | Victoria | Australia | 30.55 | 72 | NA | 63.63 | 8 |
| Solheim and associates | Ferry | Accident | 1992 | Oslo | Norway | 100 | 158 | NA | 67.72 | NA |
| Brkic and associates | War | Criminal | 1997 | Petrinja | Croatia | 58.69 | 46 | NA | 25.92 | Personal, twenty |
| Brkic and associates | War | Criminal | 2000 | Slavonia | Croatia | 82.4 | 1000 | 527 | 25 | Others, ninety one |
| Soomer and associates | Ferry | Accident | 2001 | Estonia | Europe | 11.03 | 852 | NA | 60.63 | NA |
| Dumanèiñ and associates | Train | Accident | 2002 | Zagreb | Croatia | 73.02 | 152 | 6 | 0 | Fingerprint, twenty; Personal forty two; Combination, forty nine |
| Air crash | Accident | 2002 | Vrbovec | Croatia | 94.31 | 176 | 37 | 0 | Fingerprint six; Personal fifty eight; Combination, one hundred and two | |
| Hutt and associate. | Air crash | Accident | 2005 | Strasbourg | France | 97.7 | 87 | NA | 65.88 | Other twenty nine |
| Bux and associates | Air crash | Accident | 2006 | Jomsom | Nepal | 77.77 | 18 | FO+Anthropological +Personal, 4 | 71.42 | NA |
| Tan and associates | Air crash | Accident | 2007 | Southern Sumatra | Indonesia | 5.7 | 104 | NA | 33.33 | Fingerprint two; Age, one; Personal, one |
| Prieto and associates | Terrorist attacks | Criminal | 2007 | Madrid | Spain | 100 | 191 | NA | 0 | DNA thirty one; Fingerprint one hundred forty five; Combination fifteen |
| Hinchliffe and associates | Bushfires | Natural | 2009 | Victoria | Australia | 99.42 | 173 | NA | 40.11 | NA |
| Trengrov and associates | Earthquake | Natural | 2011 | Christchurch | New Zealand | 97.79 | 181 | FO+Fingerprint+DNA, 25 | 32.76 | DNA seven; Fingerprint seventy six Physical/visual, eleven |
| Hinchliffe and associates | Air crash | Accident | 2011 | Kentucky | USA | 94 | 50 | NA | 100 | NA |
| Bush and associates | Air crash | Accident | 2011 | USA | 100 | 50 | NA | 76 | Combination twelve | |
| Manhart and associates | Vehicle | Accident | 2012 | Autobahn A19 | Germany | 100 | 8 | 0 | 0 | DNA seven; Hip implant, 1 |
| Barberia And associates | Train | Accident | 2015 | Castelldefels Platja station | Barcelona | 100 | 12 | 0 | 0 | DNA twelve; Fingerprint Eleven |
| Obafunwa and associates | Air crash | Accident | 2015 | Lagos | Nigeria | 10.13 | 152 | 133 | DNA+FO, | NA |
| Iino and associates | Tsunami | Natural | 2015 | East Japan | Japan | 99.01 | 15892 | NA | 8 | DNA one hundred fifty seven; Fingerprint, three hundred fifteen |
Results
In this systematic review data were obtained concerning the following parameters: type of study. Most of the studies were retrospective studies. It was found that maximum studies were descriptive in nature. Three different types of disasters i.e. natural, criminal, and accidental disasters were found (Table 1). Among them maximum percentage of disasters were accidental in nature (41.21%), followed by natural disasters (31.21%) and criminal disasters (27.21%). Studies included in this systematic review covered mass disasters that took place all across the globe. It included European Countries (12.21%), African countries (13.32%), Australian continent (07.21%), East Asia (14.12%), Southeast Asia (12.32%). Total numbers of victims assessed in all the studies included in this systematic review were 22345. Among them (86.21%) victims were recognized.
The percentages of victims identified by using forensic odontology alone were (15.21%) On the other hand (6.21%) victims were recognized with the help of forensic odontology along with other forensic methods. When there was analysis of other methods for reorganization of the victims in mass disasters then it was found that maximum number of victims were identified by personal visual reorganization (69.21%) followed by fingerprint (7.21%) and DNA (5.4%) (Table 2).
Table 2: Summary of the data obtained in the systematic review.
| Accidental mass disaster | 41.21% |
| Natural disasters | 31.21% |
| Criminal disasters | 27.21% |
| Mass disasters in European countries | 12.21% |
| African countries | 13.32% |
| Australia | 7.21% |
| East Asia | 14.21% |
| South East Asia | 12.32% |
| Total no of affected human beings | 22345 |
| Percentage of victims recognized | 86.21% |
| Percentage of victims recognized by forensic odontology alone | 15.21% |
| Percentage of victims recognized by forensic odontology in association with other methods | 6.21% |
| Other methods of forensic used for recognition | |
| Personal visual identification | 69.21% |
| Fingerprint | 7.21% |
| DNA | 5.40% |
Discussion
There are several reasons for death of human beings. One of the important reasons for deaths and physical inability of human beings are the mass disasters.
These are the conditions in which large number of human beings are killed or seriously injured at the same time and same place. These conditions of mass destructions are indiscriminate, violent and unexpected in nature [11,12]. These conditions are termed as MDs (Mass Disasters).
Since these conditions are very destructive therefore there is need for extensive management program to handle these conditions. These conditions of massive destruction are usually categorised in three categories: criminal, accidental, and natural. The agency authorized to study the epidemiology and carry research on the disasters have described disaster [13,14].
Disaster has been described as a condition which completely destroys a region in such a manner that help is required from the external international as well as national sources. Besides disaster is also described as condition which is unexpected and sudden in onset causing severe destruction, damage and deaths of human beings.
There have been some criteria which decide whether a condition is to be considered as disaster or not. If any one of these criteria’s are fulfilled then a condition is termed as disaster and then it is transferred in the existing database as a disaster [15,16].
One of the important part of management of such massive disasters is the reorganization of the remains found after death of human beings. This procedure is usually carried out by forensic experts.
It is very tough job because most parts of the body get damaged in massive destruction and it becomes difficult to identify the victim. There has been many methods which rely on the sufficient quantity of remains of the body for proper identification [17,18].
Nowadays forensic dentistry is also being considered for the identification of the victims in mass disasters. Forensic odontology is based on the information obtained from the teeth and Para-oral structures [19,20]. A major advantage of the forensic odontology is that the teeth of victims are not usually destroyed as compared to other parts of the body.
Therefore role of forensic odontology in mass disasters should be evaluated. Hence this systematic review was carried out to assess the role of forensic odontology in the mass disasters.
In this systemic review three different types of disasters i.e. natural, criminal, and accidental disasters were found. Among them maximum percentage of disasters were accidental in nature (41.21%), followed by natural disasters (31.21%) and criminal disasters (27.21%). Studies included in this systematic review covered mass disasters that took place all across the globe.
It included European Countries (12.21%), African countries (13.32%), Australian continent (07.21%), East Asia (14.12%), South East Asia (12.32%).
Total numbers of victims assessed in all the studies included in this systematic review were 22345. Among them 86.21%victims were recognized. The percentages of victims ide notified by using forensic odontology alone were (15.21%).
On the other hand 6.21% victims were recognized with the help of forensic odontology along with other forensic methods.
When there was analysis of other methods for reorganization of the victims in mass disasters then it was found that maximum number of victims were identified by personal visual reorganization (69.21%) followed by fingerprint (7.21%) and DNA (5.4%).
It can be summarized from the results that (15.21%) victims were recognized by forensic dentistry alone and when forensic odontology was used along with other methods then additionally (6.21%) victims were identified. Another means of classification of disasters is categorizing the disasters as closed disasters, open disasters and open disasters.
Examples of open disasters are train accidents, tsunamis and earthquakes. In open massive disasters it has been found that names of the affected human beings are normally not known.
Examples of closed disasters include those conditions where names of the involved human beings are usually known [21,22].
Some of these conditions include massive fires in the hotels, disasters involving ships and crashes of aeroplanes.
Nowadays the prevalence of massive disasters have increased due to increase in the facilities for public travelling, increase in the incidence of natural calamity and increase in terrorism [23].
In this systemic review data were obtained concerning the following parameters: type of study, nature of study, mass disaster, subtype of mass disaster i.e. natural, criminal or accidental, country where the mass disaster took place, year of incidence of mass disaster, state where the disaster took place, enumeration of total number of victims in the mass disaster, percentage of the victims who got identified, percentage of affected human victims identified with forensic odontology alone, percentage of affected human beings identified on using forensic odontology in association with other forensic methods of identification, details of other forensic methods used for reorganization of victims of the mass disasters. It can be said that forensic odontology can be used as an adjuvant in identification of victims of mass disasters. However more research will be required to establish forensic odontology as the golden standard for reorganization of victims in mass disasters.
Conclusion
It can be concluded from this systematic review that forensic odontology can be used as an adjuvant in identification of victims of mass disasters. However more research will be required to establish forensic odontology as the golden standard for reorganization of victims in mass disasters
References
- Bell G. Forensic odontology and mass disasters. N Y State Dent J 1989; 55:25-27.
- Below R, Wirtz A, Guha-Sapir D, et al. Centre for research on the epidemiology of disasters (CRED) and Munich reinsurance company (Munich RE): Disaster category classification and peril terminology for operational purposes 2009; 48.
- Nuzzolese E, Di Vella G. Future project concerning mass disaster management: a forensic odontologyprospectus. Int Dent J 2007; 57:261-266.
- Luntz LL. History of forensic dentistry. Dent Clin North Am 1977; 21:7-17.
- Bastiaan RJ. Dental identification of the Victorian bushfire victims. Aust Dent J 1984; 29:10-110.
- Solheim T, Lorentsen M, Sundnes PK, et al. The "Scandinavian Star" ferry disaster 1990Ða challenge to forensic odontology. Int J Legal Med 1992; 104:339-345.
- Brkic H, Strinovic D, Slaus M, et al. Dental identification of war victims from Petrinja in Croatia. Int J Legal Med 1997; 110:47-51.
- Brkic H, Strinovic D, Kubat M, et al. Odontological identification of human remains from massgraves in Croatia. Int J Legal Med 2000; 114.
- Soomer H, Ranta H, Penttila A, et al. Identification of victims from the M/S Estonia. Int J Legal Med 2001; 114:259-262.
- Dumanein J, Kain Z, Njemirovskij V, et al. Dental identification after two mass disasters in Croatia Croatia. Med J 2001; 42:657-662.
- Hutt JM, Ludes B, Kaess B, et al. Odontological identification of the victims of flight AI.IT 5148 air disaster Lyon-Strasbourg. Int J Legal Med 1995; 107:275-279.
- Bux R, Heidemann D, Enders M, et al. The value of examination aids in victim identification: A retrospective study of an airplane crash in Nepal in 2002. Forensic Sci Int 2006; 164:155-158.
- Schuller-Goetzburg P, Suchanek J. Forensic odontologists successfully identify tsunami victims in Phuket, Thailand. Forensic Sci Int 2007; 171:204-207.
- Tan PH, Wee KP, Sahelangi P, et al. Remembering the MusidSilkAir Flight MI 185 crash victim identification. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2007; 36:861-866. [Crossref]
- Prieto JL, Tortosa C, Bedate A, et al. The 11 March 2004 Madridterrorist attacks: The importance of the mortuary organisation for identification of victims. A critical review. Int J Legal Med 2007; 121:517-522.
- Hinchliffe J. Forensic odontology, part 3. The Australian bushfiresÐVictoria state, February 2009. Br Dent J 2011; 210:317-321.
- Trengrove H. Operation earthquake 2011: Christchurch earthquake disaster victim identification. J Forensic Odontostomatol 2011; 29:1-7.
- Hinchliffe J. Forensic odontology, part 2. Major disasters. Br Dent J 2011; 210:269-274.
- Bush M, Miller R. The crash of Colgan Air flight 3407: Advanced techniques in victim identification. J Am Dent Assoc 2011; 142:1352-1356.
- Manhart J, Bittorf A, Buttner A, et al. Disaster victim identification-experiences of the "Autobahn A19" disaster. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 2012; 8:118-124.
- Barberoaa E, Martin-Fumadoa C, Galteas I, et al. Managing the identification of the mortal victims run over by a train in the Castelldefels railwayaccident (Barcelona). Leg Med 2015; 17:366-370.
- Obafunwa JO, Ogunbanjo VO, Ogunbanjo OB, et al. Forensic odontological observations in the victims of DANA air crash. Pan Afr Med J 2015; 20:96.
- Iino M, Aoki Y. The use of radiology in the Japanese tsunami DVI process. J Forens Radiol Imag 2016; 4:20-26.
Author Info
Department of Oral Diagnostic Sciences, Riyadh Elm University, Riyadh, Saudi ArabiaCitation: Mahesh Shenoy, Role of Forensic Odontology in the Identification of Victims of Mass Disaster: A Systematic Review, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2022, 10(5): 1-6.
Received: 21-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. JRMDS-22-001; , Pre QC No. JRMDS-22-001; Editor assigned: 23-Feb-2022, Pre QC No. JRMDS-22-001; Reviewed: 09-Mar-2022, QC No. JRMDS-22-001; Revised: 22-Apr-2022, Manuscript No. JRMDS-22-001; Published: 02-May-2022
