Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 7
Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Known Diabetics with Macrovascular Complications
*Correspondence: Nishant A Tambe, Department of Ophthalmology, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, India, Email:
Abstract
Diabetic retinopathy, mainly a disorder of retinal vessels is influenced by the duration of the disease. From a total sample of 100 patients, a significant association was observed in the duration of diabetes and prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (P-value=0.000), as well as macrovascular complications of diabetes (P-value=0.001). This implies that with increasing duration of diabetes, the chances of prevalence of its complications increases. there was a significant association observed in duration of diabetes and macrovascular complications of diabetes in the group of 44 patients with diabetic retinopathy (P-value=0.049). There are studies suggesting diabetic retinopathy as a predictor of cardiovascular mortality in individuals both type 1 and type 2 DM. A positive association was not observed between the duration of diabetes and macrovascular complications of diabetes in the remaining 56 patients with no diabetic retinopathy (P-value=0.682). This suggests that presence of diabetic retinopathy can be a predictor of macrovascular complications due to diabetes.
Keywords
Diabetic retinopathy, Microvascular complicationIntroduction
Visual loss due to all the causes are preventable excepting for age related macular degeneration. Diabetes Mellitus is becoming one of the major causes of avoidable blindness. Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a micro-vascular abnormality associated with diabetes. Other micro-vascular complications are diabetic nephropathy and diabetic neuropathy. This study aims to determine the prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in known Diabetic patients, both Type 1 and Type 2, who have presented to the OPD for evaluation of Diabetic Retinopathy and its grade, having only Macro-vascular complications of diabetes elsewhere [1-3].
Materials and Methods
Study design
- Detailed history over the duration of Diabetes and treatment taken for the same and associated complications if any.
- Complete Visual Acuity check up with Snellen's Chart for distant vision and Jaegger's chart for near vision.
- Amsler Grid Test to evaluate Macular function.
- Complete Anterior segment analysis with help of Slit Lamp.
- Tropicamet Plus eye drops for complete dilatation of pupils to assess the Retina.
- Direct Ophthalmoscopy, Indirect Ophthalmoscopy with Scleral Indenter to assess the central and peripheral retina.
- 90 Dioptre lens to assess the Macula and Blood investigations - FBS, PPBS to assess the Glycemic status.
Cross-sectional study done over a sample of 100 patients. All the patients with the history of diabetes with Coronary Artery Disease, Cerebro-vascular Disease, Peripheral Arterial Disease were included in the study. Studies like Amsler grid test, complete visual activity check-up, Direct Ophthalmoscopy, Indirect Ophthalmoscopy Blood investigations - FBS, PPBS to assess the Glycemic status were performed.
Results
From among the entire sample of 100 patients with macrovascular complications 44% patients are diagnosed positive for Diabetic retinopathy and 56% patients are diagnosed negative. The association of Macrovascular complications and prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy is found to be statistically significant with a Chi Square value of 22.477 and P=0.001 (Figure 1).
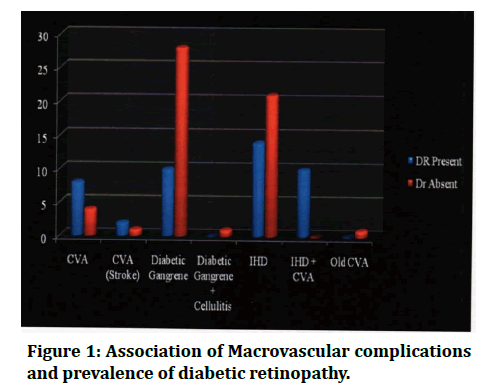
Figure 1: Association of Macrovascular complications and prevalence of diabetic retinopathy.
95.5% of the DR patients had a duration of diabetes 10.1-30 yrs. 94.6% of non-retinopathy patients, with diabetes, had duration of diabetes from 0-20 yrs. The association between duration of diabetes and diabetic retinopathy is found to be statistically significant with Chi Square value of 18.001 and P=0.000 (Figure 2).
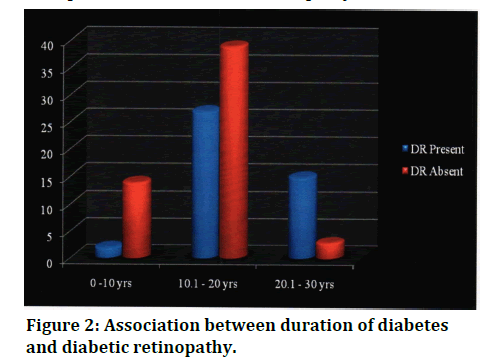
Figure 2: Association between duration of diabetes and diabetic retinopathy.
Association of duration of diabetes and diabetic retinopathy in individual macro-vascular complications
From the tables (Table 1 and Table 2) for association of duration of diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy, in in dividual macro-vascular complications, no statistically significant association is observed in the two parameters except in the group of patients with both HID and CVA where all patients were clinically diagnosed to have Diabetic Retinopathy.
Table 1: Diabetic retinopathy.
| Duration of diabetes (yrs.) | Diabetic retinopathy present | Diabetic retinopathy absent | Chi square value | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 2 | 9 | 0.966 | 0.617 |
| 10.1 - 20 | 7 | 19 | ||
| 20.1 - 30 | 1 | 1 |
Table 2: IHD+CVA.
| Duration of diabetes (yrs.) | Diabetic retinopathy present | diabetic retinopathy absent |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1-20 | 3 | 0 |
| 20.1 - 30 | 7 | 0 |
Discussion
From a total sample of 100 patients, a significant association was observed in the duration of diabetes and prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (P-value=0.000), as well as macrovascular complications of diabetes (Pvalue= 0.001). This implies that with increasing duration of diabetes, the chances of prevalence of its complications increases. This has been proved and stated by MacKinnon JR and Forrester JV [1-3]. A significant association was also established between the occurrence of Diabetic Retinopathy and macrovascular complications of diabetes (P-value=0.001). Also, there was a significant association observed in duration of diabetes and macrovascular complications of diabetes in the group of 44 patients with diabetic retinopathy (P-value=0.049).
There are studies suggesting diabetic retinopathy as a predictor of cardiovascular mortality in individuals both type 1 and type 2 DM [4-10].
Conclusion
The study concludes that increased duration of diabetes is associated with higher incidence of retinopathy as well as other macrovascular complications. Also, prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in diabetics can be used as a marker for associated macrovascular complications, thus necessitating a need of mutli-system assessment of individuals with a history of diabetes associated with retinopathy.
Funding
No funding sources.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledegements
The encouragement and support from Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, is gratefully acknowledged. For provided the laboratory facilities to carry out the research work.
References
- Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE. The wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy, II: Prevalance and high risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. Arch Ophthalmol 1984; 102:520-6.
- Horvat M, Maclean H, Goldberg L, et al. Diabetic retinopathy in pregnancy: A 12 year prospective survey. Br J Ophthalmol l980; 64:398-403.
- Moloney JB, Drury MI. The effect of pregnancy in natural course of diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1982; 93:745-56.
- Juutilainen A, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, et al. Retinopathy predicts cardiovascular mortality in type 2 diabetic men and women. Diabetes Care 2007; 30; 2:292-299
- Davis MD, Fisher MR, Gangnon RE. Risk factors for high risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy and severe visual loss: Early Treatment of diabetic retinopathy study report #18. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998; 39:233-52.
- Singh R, Gupta V, Gupta A, et al. Spontaneous closure of microaneurysm in diabetic retinopathy with treatment of coexisting anaemia. Br J Ophthalmol 2005; 89:248-9.
- Klein BE, Moss SE, Klein R. Is menarche associated with diabetic retinopathy? Diabetes Care 1990; 13:1034-8.
- Klein BE, Moss SE, Klein R. Effect of pregnancy on progression of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 1990; 13:34-40.
- Horvat M, Maclean H, Goldberg L, et al. Diabetic retinopathy in pregnancy: A 12 year prospective survey. Br J Ophthalmol l980; 64:398-403.
- Moloney JB, Drury MI. The effect of pregnancy in natural course of diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1982; 93:745-56.
Author Info
Department of Ophthalmology, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, IndiaCitation: Nishant A Tambe,Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Known Diabetics with Macrovascular Complications, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(7): 400-402
Received: 07-Jul-2021 Accepted: 22-Jul-2021
