Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 1
KAP on Status of Partially Edentulous Among Adolescents in Rural Areas (Thiruvallur District)
Yuvashree CS1 and Dhanraj Ganapathy2*
*Correspondence: Dhanraj Ganapathy, Department of Prosthodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University Tamilnadu, India, Email:
Abstract
Loss of some teeth is called partial edentulism. Those who have lost teeth are edentulous whereas those who have not lost teeth called dentate by comparison. People who are living in rural areas may follow a form of health care based on ancient traditions, beliefs, and cultural habits. Edentulism affects approximately 158 million people globally as of 2010 (2.3% of the population). It is more common in women at 2.7% compared to the male rate of 1.9%. Partial edentulism is an indication of unhealthy dental practices in society and attitude toward dental and oral care. The aim of this study was to assess the knowledge, attitude and perception on status of partially Edentulous among adolescents in rural areas in Thiruvallur District. A cross-sectional study was done by conducting a survey consisting of 10 questions prepared to assess the awareness of partial edentulism and tooth replacement among adolescents. A total of 100 participants aged between 17 and 21years in rural districts of Thiruvallur. The data were statistically analyzed. It was seen that 75% of participants were aware of the partial edentulism and can be treated. 40% of participants agreed to undergo prosthodontics treatment and rest of 25% were not aware of such treatment, and 56% of them have not undergone any treatment due to their financial issue, clinical fear. The present study concluded that the prevalence of partial edentulism among the study population was high. So, they need community-based oral health programs to increase awareness and reduce the risk of tooth loss and make them aware of prosthodontics rehabilitation among the people, and also they should be educated about the need for prosthodontics treatments
Keywords
Partial edentulous, Edentulousness, Dentate, Rehabilitations, Oral health programs
Introduction
Loss of some teeth is said to be partial edentulism, whereas loss of all teeth is called complete edentulism. People who have lost teeth are edentulous whereas those who have not lost teeth called dentate by comparison. Partial edentulousness is a dental arch in which one or more but not all natural teeth are missing. Generally the cause may be due to dental caries, periodontal disease, traumatic injuries, impactions, and supernumerary teeth, neoplastic and cystic lesion [1-3].
Partial edentulism has several drawbacks to the subjects including clinical challenges and lifestyle compromises [4,5]. Clinically, partial edentulism results in drifting and tilting of adjacent teeth, supra eruption of opposing teeth, speech alteration, changes in facial appearance and temporomandibular disorders etc. . Also, the loss and continuing degradation of the alveolar bone, the adjacent teeth and also the supporting structures will influence the difficulty to achieve an adequate restoration in a partially edentulous patient [6]. Edentulism or tooth loss affects you much more than inability to chew and digest the food properly. It has serious social, psychological and emotional consequences, which impacts the quality of life, self-image and self-esteem.
On lifestyle compromises, partial edentulism restricts intake of food, leads to weight loss. Further, it leads to lack of self -confidence, which may adversely affect the quality of life and lead to psychological dissatisfaction. There are various classification of partial edentulous arches. The possible combination of partial edentulism is more than 60,000 depending on their incidence in maxillary and mandibular arches [7]. The primary aim of the classification is to facilitate the communication about the combination of missing teeth to edentulous ridges among students, dental practitioners and laboratory techniques [8-10].
Partial edentulism is one of the important and widely studied topics in dentistry. The pattern has been evaluated in many selected populations and also in different countries. Several studies have analyzed the correlation between partial edentulism and its influencing factors like socioeconomic parameters, age, gender, etc. Few more studies also have analyzed the awareness among the subjects to replace the missing teeth [11-13]. Surveying of RPDs, patients visiting clinics, clinical records and population in a particular locality have been the most common method of evaluation of partial edentulism. Most commonly, studies have been done by recording patient details through questionnaire and then by clinical examination [14].
Previously our department has published extensive research on various aspects of prosthetic dentistry [15-25], this vast research experience has inspired us to do this survey. The aim of this survey is to assess the awareness of treatment options for partial edentulism among the rural population in Thiruvallur district and to educate them about the need for accepting prosthodontics treatment for partial edentulism.
Materials and Methods
This was a survey based study and was conducted in an online portal, survey planet. The survey was circulated among adolescents in rural areas in Thiruvallur district. This is a questionnaire based survey. The survey is conducted for 100 individuals through a link by survey planet .Adolescents were included in this survey and the results were statistically analyzed. The first set of questionnaire is based on their age , gender and their knowledge about tooth loss. The second set of questionnaire is on their difficulties in speech, pronunciation and their food habits. The third set of questionnaire is whether they are willing to undergo any implantation process and their opinion about replacement. After the collection of all data, statistical analysis was done on SPSS software version 2.0 by IBM and the chi square test was done to assess the significance of the study.
Results and Discussion
In this study 17 years of age were found to be more prevalent in partially edentulous when compared to other groups (Figure 1) with male predilection (Figure 2). The cause was found to be tooth decay than nutritional deficiency (Figure 3). Nearly 75% of the participants answered that partial edentulism can be treated (Figure 4) and they know the remedial treatment for the partial edentulism (69%) (Figure 5). Mostly 78% agreed to undergo prosthodontics treatment (Figure 6). Most of them were not undergoing any treatment due to financial issues, and fear of pain and some of them answered that they are unaware of the prosthodontics treatment (Figure 7). 78% of the participants brush once a day (Figure 8). Nearly 84% of the participants found difficulty while eating (Figure 9). By associating the age and causes for partial edentulous, It was found that tooth decay was the most common cause with more prevalent in 17 years of age (Figure 10). Pearson chi square value=119.710; p value=0.00; hence statistically significant.
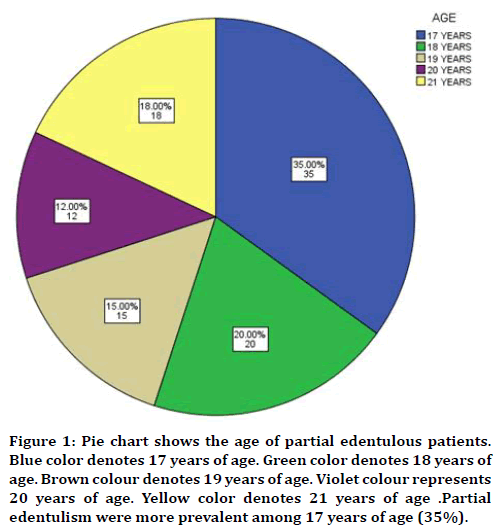
Figure 1. Pie chart shows the age of partial edentulous patients. Blue color denotes 17 years of age. Green color denotes 18 years of age. Brown colour denotes 19 years of age. Violet colour represents 20 years of age. Yellow color denotes 21 years of age .Partial edentulism were more prevalent among 17 years of age (35%).
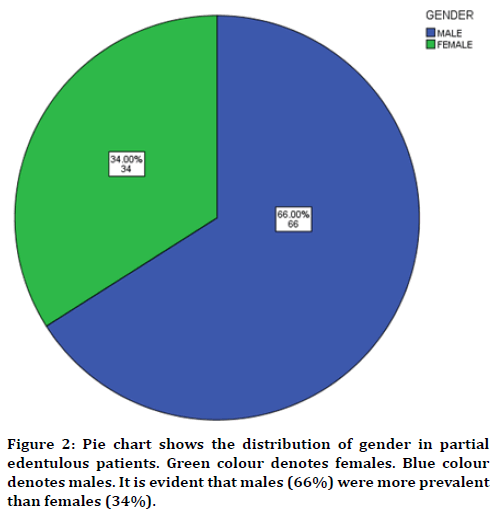
Figure 2. Pie chart shows the distribution of gender in partial edentulous patients. Green colour denotes females. Blue colour denotes males. It is evident that males (66%) were more prevalent than females (34%).
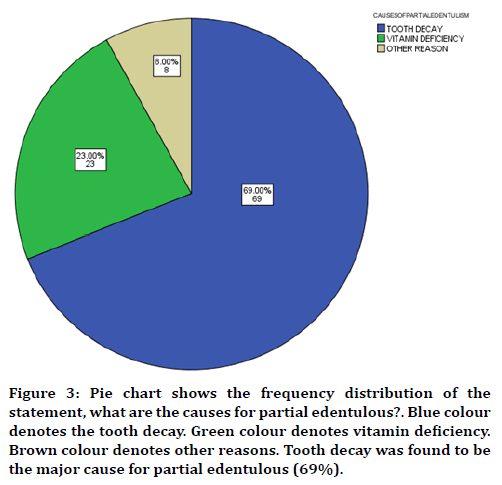
Figure 3. Pie chart shows the frequency distribution of the statement, what are the causes for partial edentulous?. Blue colour denotes the tooth decay. Green colour denotes vitamin deficiency. Brown colour denotes other reasons. Tooth decay was found to be the major cause for partial edentulous (69%).
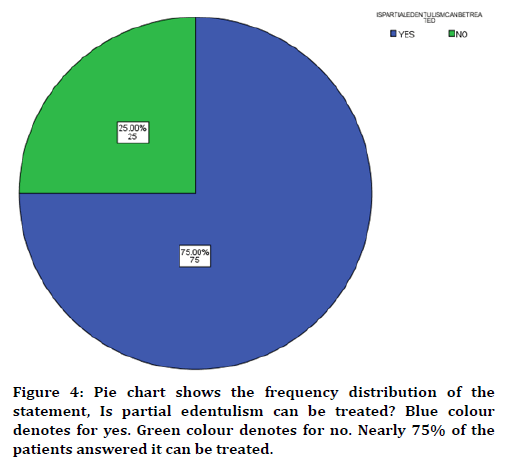
Figure 4. Pie chart shows the frequency distribution of the statement, Is partial edentulism can be treated? Blue colour denotes for yes. Green colour denotes for no. Nearly 75% of the patients answered it can be treated.
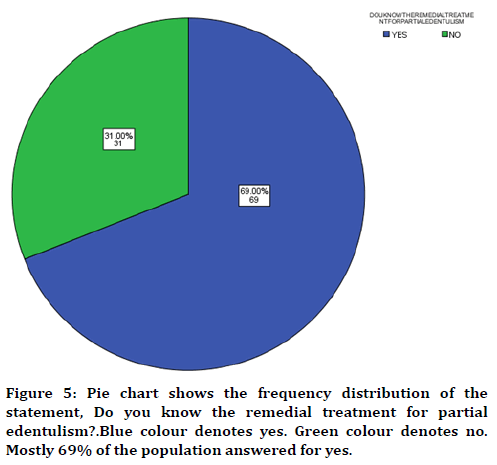
Figure 5. Pie chart shows the frequency distribution of the statement, Do you know the remedial treatment for partial edentulism?.Blue colour denotes yes. Green colour denotes no. Mostly 69% of the population answered for yes.
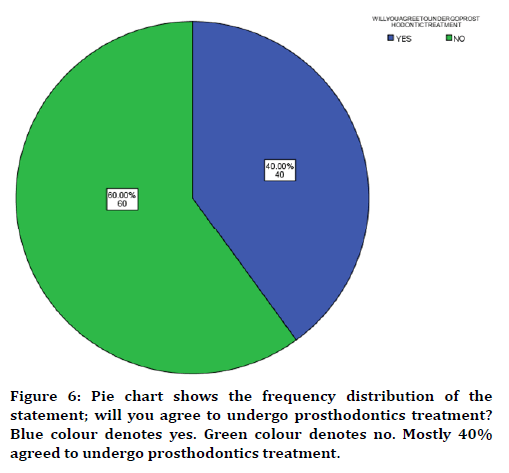
Figure 6. Pie chart shows the frequency distribution of the statement; will you agree to undergo prosthodontics treatment? Blue colour denotes yes. Green colour denotes no. Mostly 40% agreed to undergo prosthodontics treatment.
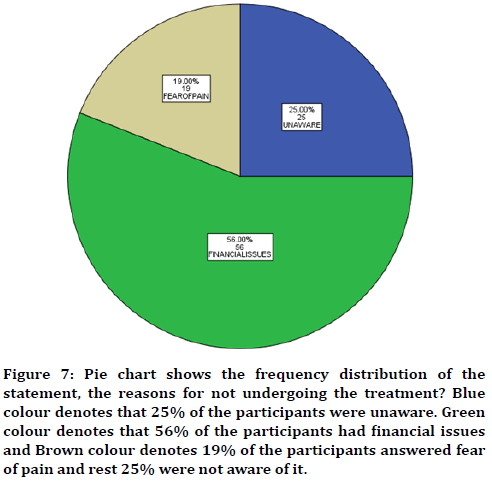
Figure 7. Pie chart shows the frequency distribution of the statement, the reasons for not undergoing the treatment? Blue colour denotes that 25% of the participants were unaware. Green colour denotes that 56% of the participants had financial issues and Brown colour denotes 19% of the participants answered fear of pain and rest 25% were not aware of it.
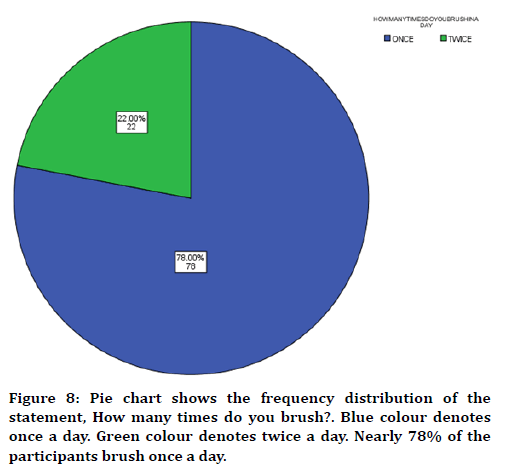
Figure 8. Pie chart shows the frequency distribution of the statement, How many times do you brush?. Blue colour denotes once a day. Green colour denotes twice a day. Nearly 78% of the participants brush once a day.
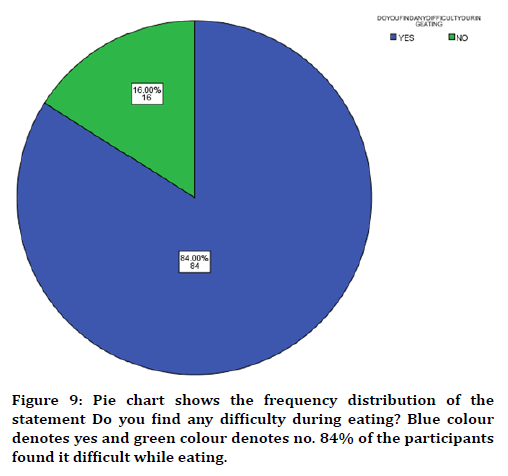
Figure 9. Pie chart shows the frequency distribution of the statement Do you find any difficulty during eating? Blue colour denotes yes and green colour denotes no. 84% of the participants found it difficult while eating.
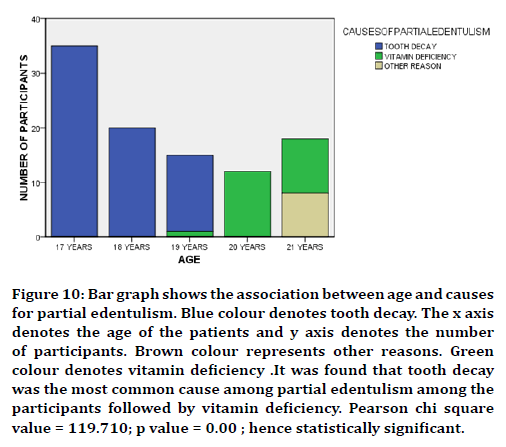
Figure 10. Bar graph shows the association between age and causes for partial edentulism. Blue colour denotes tooth decay. The x axis denotes the age of the patients and y axis denotes the number of participants. Brown colour represents other reasons. Green colour denotes vitamin deficiency .It was found that tooth decay was the most common cause among partial edentulism among the participants followed by vitamin deficiency. Pearson chi square value = 119.710; p value = 0.00 ; hence statistically significant.
Edentulism results when one or more teeth are missing, or removed due to any injury or some other diseases which occur in the oral cavity. With full edentulism, all teeth present in the oral cavity are lost, in cases of partial edentulism, one or more teeth are missing. In this study 17 years of age were found to be more prevalent in partially edentulous when compared to other age groups (Figure 1) with Male predilection (Figure 2). The cause was found to be tooth decay than nutritional deficiency (Figure 3). Many studies have consistently shown that the major cause for tooth loss is due to the role of some specific oral diseases like dental caries and periodontal disease [26].
Nearly 75% of the participants answered that partial edentulism can be treated (Figure 4) and they know the remedial treatment for it (69%) (Figure 5). Mostly 78% agreed to undergo prosthodontics treatment (Figure 6). Most of them were not undergoing any treatment due to financial issues, and fear of pain and some of them answered that they are unaware of the prosthodontics treatment (Figure 7). Partial edentulism depends on socio-economic parameters like family income, education, occupation, etc. Partial edentulism decreases in the employed group. The lower income group people could not afford the treatment procedures due to their financial issues that would have saved their questionable teeth, but they might have opted for extraction instead of prosthetic treatment. Less educated people were not aware about oral health care. People with better employment status are more concerned about their aesthetics and oral health and they opt for dental treatment [13,27].
78% of the participants brush once a day (figure 8)). Nearly 84% of the participants found difficulty while eating (Figure 9). It was found that tooth decay was the most common cause among partial edentulism among the participants followed by vitamin deficiency (Figure 10). The primary purpose of using RPDs classification is to simplify the description of potential combinations of teeth to ridges. Edentulism or tooth loss affects much more in ability to chew and properly digest food. It has serious social, psychological and emotional consequences, impacting your quality of life ,self-image and self-esteem [7,28].
Socio economic parameters have direct influence on the replacement of missing teeth; It is evident that due to lack of motivation it was found to be the most common reason for not seeking dental treatment [29]. According to a study done by Judy et al., it was evident that partial edentulism were more common among males than females [30]. Some studies have analyzed the correlation between partial edentulism and factors such as educational status and socioeconomic statuses [31]. The study conducted by D’Souza et al., in which the partial edentulism was correlated with various sociodemographic factors [13,32]. The study conducted by Sapkota et al. in his study correlated the employment status, and studied the prevalence and awareness of tooth replacement among people [33].
Conclusion
The prevalence of partial edentulism in the study population from rural (Thiruvallur area) is relatively high .The awareness about rehabilitation of partial edentulous state is also inadequate. Hence, more awareness on partial edentulism and treatment programmers need to be initiated to address this concern.
Acknowledgment
The authors of this study would like to express their gratitude towards everyone who facilitated and enabled us to carry out this study successfully.
Conflict of Interest
There were no conflicts of interest as declared by the authors.
References
- Lekholm UL, Gunne J, Henry P, et al. Survival of the Brånemark implant in partially edentulous jaws: a 10-year prospective multicenter study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1999; 14:639-645.
- Zaigham AM, Muneer MU. Pattern of partial edentulism and its association with age and gender. Pakistan Oral Dent J 2010; 30.
- Lee BR, Kim JH. Rehabilitation of maxillary partial edentulous patients using implant assisted removable partial denture. J Korean Academy Prosthodont 2014; 52.
- Abdurahiman VT, Khader MA, Jolly SJ. Frequency of partial edentulism and awareness to restore the same: A cross sectional study in the age group of 18–25 years among kerala student population. J Indian Prosthodont Society 2013; 13:461-465.
- Saleh MM, Tahir CD, Abdel-Rahman HK. Incidence of partial edentulism and its relation with age and gender. Zanco J Med Sci 2013; 17:463-470.
- McGarry TJ, Nimmo A, Skiba JF, et al. Classification system for partial edentulism. J Prosthodont 2002; 11:181-193.
- Naveed H, Aziz MS, Hassan A, et al. Patterns of partial edentulism among armed forces personnel reporting at armed forces institute of dentistry Pakistan. Pakistan Oral Dent J 2011; 31.
- Murphy WM. Removable partial denture design. J Dent 1981; 247.
- Curtis DA, Curtis TA, Wagnild GW, et al. Incidence of various classes of removable partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent 1992; 67:664-667.
- Keyf F. Frequency of use of the various classes of removable partial dentures and selection of major connectors and direct/indirect retainers. Turkish J Med Sci 2001; 31:445-449.
- Esan TA, Olusile AO, Akeredolu PA, et al. Socio-demographic factors and edentulism: The Nigerian experience. BMC Oral Health 2004; 4:3.
- Khalil A, Hussain U, Iqbal R, et al. Patterns of partial edentulism among patients reporting to department of prosthodontics, Khyber college of dentistry, Peshawar. JKCD 2013; 3:42-45.
- D'Souza KM, Aras M. Association between socio-demographic variables and partial edentulism in the Goan population: An epidemiological study in India. Indian J Dent Res 2014; 25:434.
- AL-Dwairi ZN. Partial edentulism and removable denture construction: a frequency study in Jordanians. Eur J Prosthodont Restorative Dent 2006; 14:13-17.
- Begum R, Ariga P, Jain AR. Evaluation of corrosive behavior of four nickel–chromium alloys in artificial saliva by cyclic polarization test: An in vitro study. World J Dent 2017; 8:477-482.
- Ganapathy DM, Kannan A, Venugopalan S. Effect of coated surfaces influencing screw loosening in implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Dent 2017; 8:496–502.
- Jain AR. Clinical and functional outcomes of implant prostheses in fibula free flaps. World J Dent 2017; 8:171–176.
- Jain AR. Prevalence of partial edentulousness and treatment needs in rural population of South India. World J Dent 2017; 8:213–217.
- Ranganathan H, Ganapathy DM. Jain AR. Cervical and incisal marginal discrepancy in ceramic laminate veneering materials: A SEM analysis. Contemporary Clin Dent 2017; 8:272–278.
- Jain AR, Nallaswamy D, Ariga P, et al. Determination of correlation of width of maxillary anterior teeth using extraoral and intraoral factors in Indian population: A systematic review. World J Dent 2018; 9:68-75.
- Gupta P, Ariga P, Deogade SC. Effect of monopoly-coating agent on the surface roughness of a tissue conditioner subjected to cleansing and disinfection: A contact profilometric in vitro study. Contemporary Clin Dent 2018; 9:S122.
- Anbu RT, Suresh V, Gounder R, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of three different bone regeneration materials: An animal study. Eur J Dent 2019; 13:22.
- Ashok V, Ganapathy D. A geometrical method to classify face forms. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 2019; 9:232-235.
- Duraisamy R, Krishnan CS, Ramasubramanian H, et al. Compatibility of nonoriginal abutments with implants: Evaluation of microgap at the implant–abutment interface, with original and nonoriginal abutments. Implant Dent 2019; 28:289-295.
- Varghese SS, Ramesh A, Veeraiyan DN. Blended module‐based teaching in biostatistics and research methodology: A retrospective study with postgraduate dental students. J Dent Educ 2019; 83:445-450.
- Zhang DG, Chen RR, Li CQ, et al. Clinical using and observation of occlusion splint of RPD. Shanghai J Stomatol 2004; 13:230-232.
- Al Moaleem MM, Somaili DM, Ageeli TA, et al. Pattern of partial edentulism and its relation to age, gender, causes of teeth loss in Jazan population. Am J Health Res 2016; 4:121-126.
- Araby YA, Almutairy AS, Alotaibi FM. Pattern of partial edentulism in correlation to age and gender among a selected Saudi population. Int J Dent Sci Res 2017; 5:1-4.
- Nallaswamy D. Textbook of prosthodontics. JP Medical Ltd. 2017.
- Judy HJ. The incidence of frequency of a various removable partial edentulism cases. Mustansiriya Dent J 2018; 6:172-177.
- Şakar O. Current status on partial edentulism and removable partial dentures. Springer Removable Partial Dentures 2016; 3-8.
- Compagnoni MA, Souza RF, Leles CR. Kinesiographic study of complete denture movement related to mucosa displacement in edentulous patients. Pesquisa Odontológica Brasileira 2003; 17:356-361.
- Sapkota B, Adhikari B, Upadhaya C. A study of assessment of partial edentulous patients based on kennedy’s classification at Dhulikhel Hospital Kathmandu University Hospital. Kathmandu University Med J 2013; 11:325-327.
Author Info
Yuvashree CS1 and Dhanraj Ganapathy2*
1Undergraduate student, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University Tamilnadu, Chennai, India2Department of Prosthodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University Tamilnadu, Chennai, India
Citation: Yuvashree CS1, Dhanraj Ganapathy, KAP on Status of Partially Edentulous Among Adolescents in Rural Areas (Thiruvallur District), J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9 (1): 333-338.
Received: 23-Sep-2020 Accepted: 11-Jan-2021
