Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 1
Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Biogenic Gold Nanoparticles
K Ajith Kamath, Iffat Nasim* and S Rajesh
*Correspondence: Iffat Nasim, Department Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University Tamilnadu, India, Email:
Abstract
Gold nanoparticles are some among the most researched nanomaterials in the field of nanotechnology. They can be easily synthesised and show excellent chemical as well as thermal stability. Biosynthesized nanoparticles offer excellent biocompatibility compared to nanoparticles synthesized by any other physicochemical methods. The main objective of this study was to analyze the antimicrobial activity of the gold nanoparticles synthesised with aspartic acid and to evaluate its cytotoxicity at the embryonic level. The antimicrobial activity of the AuNPs was assessed by the well diffusion method using different clinical pathogenic bacteria namely, E faecalis, S.mutans, Pseudomonas, and S. aureus. Zebrafish were selected for this study to analyze the cytotoxicity of the AuNPs. The zone of inhibition was seen to be the largest in E. faecalis(20mm) and smallest in S.aureus (9mm). When compared to the control antibiotics, Ampicillin (1mg/ml), the zone of inhibition was larger in the S mutans (18mm) at 100μg/mL followed by Pseudomonas (12mm zone) at100μg/mL. It was seen that mortality rate proportionally increased as the concentration of the solution of AuNPs increased. The AuNPs showed considerable antimicrobial property when tested against various pathogenic strains of bacteria. The AuNPs however showed to be dose dependent cytotoxic in nature. More studies need to be undertaken to establish optimum concentrations of AuNPs to have minimum negative effects on the host and best deliver its therapeutic purpose.
Keywords
UTI, Urinary tract disease, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Urethritis, Cystitis, Prostatitis
Introduction
Urinary tract disease has been depicted since antiquated occasions with the principal reported portrayal in the Ebers Papyrus dated to 1550 BC1.
It was depicted by Egyptians as "Sending forward warmth from the bladder 2. The principal instance of UTI was recorded by John Arden in Britain. Later in 1863, Pasteur has perceived pee as a decent culture media for microorganisms and related the nearness of microscopic organisms in the pee to manifestations, yet next to no advance was made in investigating the relationship until quantitative evaluations of the quantity of microbes in the pee of patients with urinary tract contamination were done by numerous creators. In 1995, Quantitative bacterial tallying more than 105 microorganisms for every ml was viewed as ture or critical bacteriuria by Kass et al. idea [1-4]
The anti-toxin time of Goodman and Gillman began with the disclosure of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928. As indicated by Patricia A Bradford (2001)4 rise of protection from β lactam antibiotics started even before the first β-Lactam penicillin was created [5-8]. The first β-Lactam anti-infection was recognized in E. coli preceding the arrival of penicillin in medicinal practice. Numerous genera of gram-negative microorganisms have a normally happening chromosomally intervened β lactamase. These catalysts are thought to have developed from penicillin restricting protein with which they give some grouping homology. In the mid- 1940s saved by the requirement for hostile to bacterial operators in World War II penicillin was found not exclusively to fix disease yet in addition to have low poisonous quality. This advanced the assistant quest for comparative enemy of microbial specialists. Immediately after the penicillin got accessible for treatment; compounds ready to pulverize penicillin named penicillinases were identified in E. coli.
Datta et al. [5] portrayed the first plasmid interceded β lactamase in Gram negative microbes; TEM-1 was depicted in the mid- 1960s. According to Mederos et al. [6], the TEM- 1 protein was initially found in a solitary strain of E. coli disconnected from a blood culture from a patient named Temoniera in Greece, thus the Designation TEM [9-11].
Mendell et al7 clarified another regular plasmid interceded β lactamse found in Klebsiella pneumonia and E. coli; SHV1 (for sulfhdryl variable). The SHV 1 β-lactamase is chromosomally encoded in most of detaches in Klebsiella however is typically plasmid intervened in E.coli.
Numerous new β-lactam anti-toxins have been built up that were explicitly intended to be impervious to the hydrolutic activity of β lactamases. To defeat the β-lactamase intervened obstruction against penicillin delivered by Gram negative microorganisms, expansive range antiinfection agents like penicillin and ampicillin were acquainted with clinical practice in 1950s. In the year 1960s the first era cephalosporin arrived at the market. The expansive range penicillin and the first era cephalosporin remained the first line of treatment for right around 20 years. With each new class of β lactam anti-infection agents that have been utilized to treat patients, another β lactamase develops. This reason protection from all class of medications. One of the new class was Oximino-cephalosporin which turned out to be generally utilized for the treatment of genuine disease because of Gram negative microscopic organisms in 1980s. Protection from third era expanded range β-lactam anti-infection agents due to β-lactamases rose rapidly. As a result of increment range of movement against the Oximino-cephalosporins the chemicals were called Extended range β lactamases (ESBL). Today more than 150 distinctive ESBLs have been depicted.
Classification of urinary tract infection (UTI)
Lower UTI
Urethritis: Infection of the urethra which presents as dysurea and increased frequency of urination
Cystitis: Infection of the urinary bladder with features of dysurea, frequency, urgency, and supra pubic tenderness.
Acute urethral syndrome: Youthful explicitly dynamic ladies with dysurea, recurrence and desperation however yield life form < 105CFU/ ml
Prostatitis: Inection of the prostate.
Upper UTI
Pyelonephritis: inflammation of the kidney, parenchyma, calyx and pelvis caused by bacterial infection.
Urethritis: Rare, usually due to tuberculosis.
Types of UTI
Uncomplicated UTI alludes to contamination in a fundamentally and neurologically typical urinary tract.
Complicated UTI alludes to contamination in a urinary tract with useful or basic variations from the norm.
Relapses repeat of bacteriuria with the equivalent contaminating small scale life forms that was available before treatment was begun because of tirelessness of the living being in the urinary tract
Reinfection Recurrence of bacteria with microorganisms different from the original infective bacteria.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria Isolation of significant count of bacteria from a person without signs and symptoms of UTI.
Epidemiology of urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infections are the commonest infection encountered in the community. In females, 1-3% schoolgirls are commonly affected by UTI and then markedly with the onset of sexual activity and it is the most common among women between 20-50 years of age. In males, acute asymptomatic infections occur in first year of life often in association with urologic abnormalities; therafter UTI’s are unusual in male patients under the age of 50.
Pathogenesis of urinary tract infection (Figure 1) Route of Infection
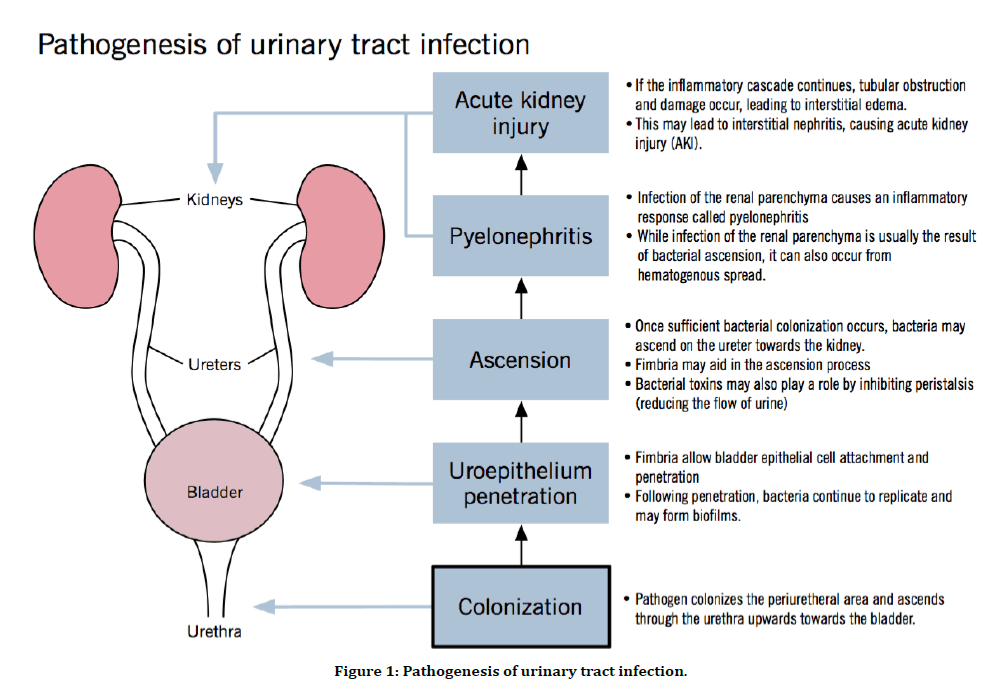
Figure 1. Pathogenesis of urinary tract infection.
Urine is a sterile fluid. The bacteria can invade and cause UTI via two major routes.
Ascending route.
Descending route.
Ascending route is the commonest route of infection in females. Catherterization and cystoscopy can cause UTI in both males and females by ascending route. Descending route of infection is caused by hematogenous spread as result of bacteremia.
Host defence against UTI
Urine is inhibitory to anaerobic bacteria and the low pH, high osmolarity, high organic acid content and constant flushing action of urine inhibit the bacterial colonization.
Valve like membranes at the junction of the bladder and ureter that prevents back flow of urine.
Immune system- Lipopolysaccharide of bacteria activates the host cell and release cytokines such as TNF α and TNF γ, activation of complement system.
Tamm-Horsfall protein or uromucoid serves as anti-adhesion factor by binding to E. coli, expressing type I fimbriae.
Defensins-group of small antimicrobial peptides produced by macrophages, neutrophils and cells in the urinary tract and attached to the bacterial cell eventually kill the bacteria.
Predisposing factors
The Following factors help in the development of UTI
Any variation from the norm of the urinary tract that impedes or eases back the progression of pee for instance Tumor, stricture and in men developed prostate can discourage the pee stream and make contamination hard to treat.
UTI happen in little level of newborn children because of inborn anomaly that requires medical procedure.
People on Immuno suppressive state like Diabetes Mellitus.
UTI is more common in females because of short urethra that opens into the moist introitus which is colonized by bacteria. For many women sexual intercourse precipitates UTI. Women using Diaphragm or spermicides as a contraceptive measure are likely to develop UTI than other forms of contraception.
Pregnant ladies are increasingly vulnerable to UTI's because of check to pee stream brought about by hormonal changes and furthermore because of weight on the urinary tract.
Post-menopausal women due to estrogen deficiency and with uterus prolapsed
Patients with Neurogenic bladder like spinal line damage, sexually transmitted disease, numerous sclerosis and diabetes mellitus or bladder diverticulum.
Conclusion
Virulence Factors for E. coli
Fimbria which binds on uroepithelium persists within the urinary tract. Three types are Type “S” fimbriae, Type “P” fimbriae and Type “D” fimbriae. Others are Toxins-haemolysin, siderophores. Uropathogenic strain specific proteins, protections, TIR domain containing proteins (tcp C) intimin, Colonising factor-CFA I, II and III.
Ethical Clearance
Nil.
Source of Funding
Self-funded.
Conflict of Interest
Nil.
References
- Sharon M. A peep into what was behind the incorporation of gold nano particles in nano medicine. J Nanomed Res 2015; 2:00022.
- Abdelâ?Majied Alâ?Sherbini A, Atta Khedr M. Laser induced ablation of gold nano particles in micellar solution. In AIP Conference Proceedings 2005; 748:268-274.
- Purushotham E. Fabrication and characterization of gold nano particles. J Adv Physics 2014; 3:309-311.
- Shaikh SM, Shaikh TJ. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver and Gold Nano Particles using Fungal Species. Plantae Scientia. 2018 May 15;1(01):25-30.
- Shaikh SM, Shaikh TJ. Biogenic synthesis of silver and gold nano particles using fungal species. Plantae Scientia 2018; 1:25-30.
- Kumar N, Balamurugan A, Balakrishnan P, et al. Biogenic nanomaterials: Synthesis and its applications for sustainable development. InBiogenic Nano-Particles and their Use in Agro-ecosystems. Springer, Singapore 2020; 99-132.
- Govindaraju L, Neelakantan P, Gutmann JL. Effect of root canal irrigating solutions on the compressive strength of tricalcium silicate cements. Clin Oral Invest 2017; 21:567-71.
- Azeem RA, Sureshbabu NM. Clinical performance of direct versus indirect composite restorations in posterior teeth: A systematic review. J Conservative Dent 2018; 21:2â??9.
- Jenarthanan S, Subbarao C. Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of diclofenac sodium administered using different delivery routes in the management of endodontic pain: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J Conservative Dent 2018; 21:297â??301.
- Manohar MP, Sharma S. A survey of the knowledge, attitude, and awareness about the principal choice of intracanal medicaments among the general dental practitioners and nonendodontic specialists. Indian J Dent Res 2018; 29:716â??720.
- Nandakumar M, Nasim I. Comparative evaluation of grape seed and cranberry extracts in preventing enamel erosion: An optical emission spectrometric analysis. J Conservative Dent 2018; 21:516â??520.
- Teja KV, Ramesh S, Priya V. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-3 gene expression in inflammation: A molecular study. J Conservative Dent 2018; 21:592â??596.
- Janani K, Sandhya R. A survey on skills for cone beam computed tomography interpretation among endodontists for endodontic treatment procedure. Indian J Dent Res 2019; 30:834â??838.
- Khandelwal A, Palanivelu A. Correlation between dental caries and salivary albumin in adult population in Chennai: An In Vivo study. Brazilian Dent Sci 2019; 22:228â??233.
- Malli Sureshbabu N, Selvarasu K, Nandakumar M, et al. Concentrated growth factors as an ingenious biomaterial in regeneration of bony defects after periapical surgery: A report of two cases. Case Reports Dent 2019; 2019.
- Poorni S, Srinivasan MR, Nivedhitha MS. Probiotic strains in caries prevention: A systematic review. J Conservative Dent 2019; 22:123â??128.
- Rajakeerthi R, Ms N. Natural product as the storage medium for an avulsed toothâ??A systematic review. Cumhuriyet Dent J 2019; 22:249â??256.
- Rajendran R, Kunjusankaran RN, Sandhya R, et al. Comparative evaluation of remineralizing potential of a paste containing bioactive glass and a topical cream containing casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate: An in Vitro study. Pesquisa Brasileira Odontopediatria Clin Integrada 2019; 19:1-10.
- Ramarao S, Sathyanarayanan U. CRA grid-A preliminary development and calibration of a paper-based objectivization of caries risk assessment in undergraduate dental education. J Conservative Dent 2019; 22:185â??190.
- Siddique R, Nivedhitha MS. Effectiveness of rotary and reciprocating systems on microbial reduction: A systematic review. J Conservative Dent 2019; 22:114â??122.
- Siddique R, Sureshbabu NM, Somasundaram J, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of precipitate formation following interaction of chlorhexidine with sodium hypochlorite, neem, and tulsi. J Conservative Dent 2019; 22:40.
- Siddique R, Nivedhitha MS, Jacob B. Quantitative analysis for detection of toxic elements in various irrigants, their combination (precipitate), and para-chloroaniline: An inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry study. J Conservative Dent 2019; 22:344-350.
- Yang F, Zhang Q, Guo H, et al. Evaluation of cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and teratogenicity of marine sediments from Qingdao coastal areas using in vitro fish cell assay, comet assay and zebrafish embryo test. Toxicology 2010; 24:2003-2011.
- Kumar V, Yadav SK. Plantâ?mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 2009; 84:151-157.
- Njoki PN, Lim II, Mott D, et al. Size correlation of optical and spectroscopic properties for gold nanoparticles. J Physical Chem 2007; 111:14664-14669.
- Cohen FL, Tartasky D. Microbial resistance to drug therapy: A review. Am J Infection Control 1997; 25:51â??64.
- Harbottle H, Thakur S, Zhao S, et al. Genetics of antimicrobial resistance. Animal Biotechnol 2006; 17:111-124.
- Singh R. Are cytotoxicity tests in biological studies reliable? Bio Sci Res Bulletin 2018; 34:36-39.
Author Info
K Ajith Kamath, Iffat Nasim* and S Rajesh
1Department Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University Tamilnadu, Chennai, IndiaCitation: K Ajith Kamath, Iffat Nasim, S Rajesh, Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Biogenic Gold Nanoparticles, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9 (1): 274-278.
Received: 23-Sep-2020 Accepted: 01-Jan-2021
