Research - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 7
Effect of Dexmedetomidine for Haemodynamic Stability in Laparoscopic Surgeries
*Correspondence: M Rekha, Department of Anaesthesiology, pain Medicine and Critical Care, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, India, Email:
Abstract
Two groups were formed, one received dexmedetomidine 1mcg /kg infusion for 15 minutes and other received saline0.9%. The heart rate was 73.90 ± 10.81 in group received dexmedetomidine against 91.53 ± 15.63 in the control group after Co 2 insufflation. Mean heart rate was 85(17) which fell to lowest of 72(13); p=0.0001. The mean systolic blood pressure was 125.37 ± 17.95 and diastolic blood pressure was 83.53 ± 12.35 after creation of pneumoperitoneum which was statistically significant. after creation of pneumoperitoneum, the heart rate was significantly decreased 76.17 ± 10.27 compared to the control group.
Keywords
Pneumoperitoneum, Mean heart rate
Introduction
Dexmedetomidine belongs to alpha-2 adrenoreceptor agonist group of drugs. Compared to other existing drugs they are more specific for alpha 2 receptors. when a laparoscopic surgery is performed a pneumoperitoneum should is created by insufflation with air or carbon dioxide. The created pneumoperitoneum causes several pathophysiological changes during the surgery [1-4]. To avoid such complications and obtain hemodynamic stability various drugs have been used such as clonidine and dexmedetomidine. They have the potential to maintain the blood pressure during laparoscopic surgeries. Hence this study deals with the action of one such drug, dexmedetomidine on the hemodynamic stability during laparoscopic surgeries.
Methodology
Patients (60Nos) of ASA I & II physical status aged 18-60 years were selected who were scheduled to undergo elective laparoscopic surgeries. They were randomized and allotted into two groups (D&F). Group D received dexmedetomidine 1 mcg/kg infusion before induction (n=30) with propofol 2mg/kg IV and fentanyl l mcg/kg IV- (n=30) Group F received fentanyl lmcg/kg with propofol 2mcg/kg IV (n=30). Then the hemodynamic stability during the surgery were assessed for the following parameters-Heart rate, blood pressure and oxygen saturation were observed and recorded at baseline, after dexmedetomidine infusion, after induction, insufflation of Co2, at 30 and 45 mins and after extubating.
Results
Heart rate was compared before induction, after induction, after carbon dioxide insufflation, after 30 minutes, 45 mins, after extubation was compared in both groups and tabulated in Table 1.
Table 1: Heart rate comparison.
| Variables | Dexmed | Fentanyl | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | ||
| Basal | 60-112 | 82.9 ± 12.23 | 63-110 | 86.2 ± 12.7 | 0.309 |
| After induction | 55-90 | 74.17 ± 12.79 | 60-118 | 80.23 ± 14.02 | 0.06 |
| Co2 insufflations | 54-104 | 76.17 ± 10.27 | 70-118 | 89.87 ± 3.31 | P<0.001 |
| After 30 min | 55-102 | 79.03 ± 12.62 | 68-124 | 89.43 ± 12.44 | 0.001** |
| After 45 min | 55-110 | 77.8 ± 11.4 | 60-124 | 85.97 ± 12.25 | 0.009** |
| After Extubation | 60-95 | 79.27 ± 8.87 | 62-106 | 84.27 ± 10.02 | 0.04* |
| P-value | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | |||
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure was compared before induction, after induction, after carbon dioxide insufflation, after 30 minutes, 45 mins, after extubating was compared in both groups (Figures1 and 2).
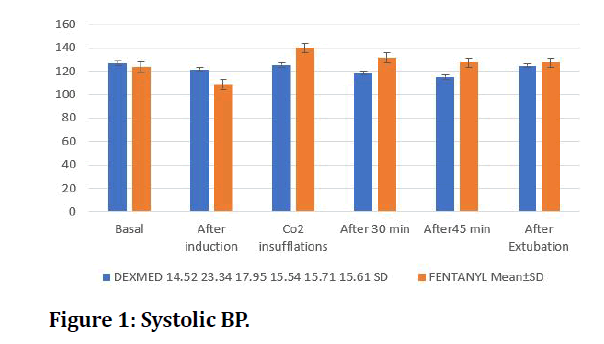
Figure 1: Systolic BP.
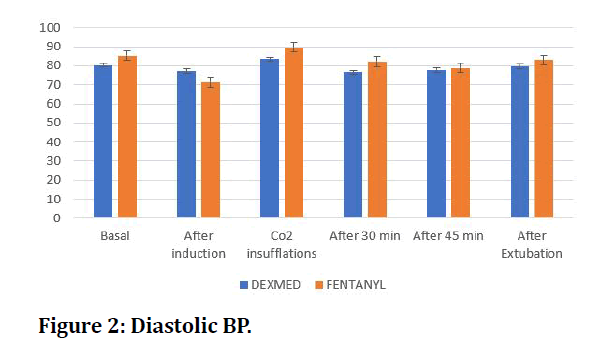
Figure 2: Diastolic BP.
Mean blood pressure and oxygen saturation was also compared between two groups and there were not much difference and results are tabulated (Tables 2 and 3).
Table 2: Mean blood pressure.
| Variables | Dexmed | Fentanyl | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | ||
| Basal | 68-120 | 93.73 ± 12.96 | 68-137 | 100.47 ± 15.61 | 0.074 |
| After induction | 65-133 | 93.93 ± 16.03 | 62-104 | 84.57 ± 9.76 | 0.008** |
| Co2 insufflations | 73-129 | 98.37 ± 13.59 | 74-137 | 106.37 ± 14.24 | 0.029* |
| After 30 min | 74-119 | 91.07 ± 12.34 | 65-125 | 98.33 ± 14.02 | 0.037* |
| After45 min | 65-137 | 91 ± 14.05 | 76-126 | 96 ± 12.58 | 0.15 |
| After Extubation | 73-122 | 95.67 ± 11.48 | 73-126 | 97.37 ± 10.18 | 0.546 |
| P-value | 0.024* | P<0.001*** | |||
Table 3: Oxygen saturation.
| Variables | Dexmed | Fentanyl | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | ||
| Basal | 97-100 | 98.77 ± 0.94 | 81-100 | 98.3 ± 3.38 | 0.501 |
| After induction | 98-100 | 99.93 ± 0.36 | 100-100 | 100 ± 0 | 0.322 |
| Co2 insufflations | 98-100 | 99.9 ± 0.55 | 100-100 | 100 ± 0 | 0.321 |
| After 30 min | 97-100 | 99.87 ± 0.57 | 100-100 | 100 ± 0 | 0.206 |
| After 45 min | 97-100 | 99.87 ± 0.57 | 100-100 | 100 ± 0 | 0.206 |
| After Extubation | 98-100 | 99.9 ± 0.402 | 100-100 | 100 ± 0 | 0.179 |
| P-value | P<0.001 | 0.01* | |||
Discussion and Conclusion
This study elaborates the effects of dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic. Stability in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgeries and when the results are compared with the similar study done by Khare et al. [2] there was transient fall in heart rate at beginning of dexmedetomidine infusion however sustained entire duration of infusion. Patients had sinus bradycardia (HR<60) at start, but none required treatment. Mean systolic blood pressure was 125 (22) at start and fell to 113(20) with dexmedetomidine but in this study mean heart rate was ranging from 54 to a maximum of 112. The patients did not require any treatment for the bradycardia. The effect of single preoperative dose of dexmedetomidine on the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation, perioperative hemodynamics and anaesthetic requirements [3-10]. The blood pressure and heart rate were significantly lower (p<0.05) in the dexmedetomidine group which is like our study wherein after creation of pneumoperitoneum, the heart rate was significantly decreased 76.17 ± 10.27 compared to the control group. The systolic blood pressure was 125.37 ± 17.95 and diastolic blood pressure is 83.53 ± 12.35 compared to the compared to control group which was sbp 139.87 ± 18.33 and dbp 89. 73 ± 12.51 which was significant. These results were consistent with our results.
References
- Keniya VM, Ladi S, Naphade R. Dexmedetomidine attenuates sympathoadrenal response to tracheal intubation and reduces perioperative anaesthetic requirement. Indian J Anaesthesia 2011; 55:352.
- Khare A, Sharma SP, Deganwa ML, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine on intraoperative hemodynamics and propofol requirement in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesthesia Essays Res 2017; 11:1040.
- Gertler R, Brown HC, Mitchell DH, et al. Dexmedetomidine: a novel sedative-analgesic agent. InBaylor University Medical Center Proceedings Taylor & Francis 2001.
- Kallio A, Scheinin M, Koulu M, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine, a selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, on hemodynamic control mechanisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1989; 46:33-42.
- Bloor BC, Ward DS, Belleville JP, et al. Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine in humans Hemodynamic changes. Anesthesiol 1992; 77:1134-42.
- Gertler R, Brown HC, Mitchell DH, et al. Dexmedetomidine: A novel sedative-analgesic agent. InBaylor University Medical Center Proceedings 2001; 14:13-21.
- Hayashi Y, Maze M. Alpha2 adrenoceptor agonists and anaesthesia. BJA: British J Anaesthesia 1993; 71:108-18.
- Stoelting RK. Text book of pharmacology & physiology in anaesthesia practice. 4th Edn, Churchil Livingtone 2008.
- Recep Aksu, Ayur Akin, Cihangir, et al. Comparision of the effects of dexmedetomidine versus fentanyl on airway reflexes and hemodynamic responses to tracheal extubation during rhinoplasty. Current Therap Res 2009; 209-20.
- Kallio A, Scheinin M, Koulu M, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine, a selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, on hemodynamic control mechanisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1989; 46:33-42.
