Research Article - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 12
Assessment of Knowledge Regarding Diabetic Complication among Adults
*Correspondence: AR. Bharathi, Department of Nursing, Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Selaiyur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, Email:
Abstract
A study to assess type 2 diabetic patient with inadequate glycemic control on oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA) or a lifestyle intervention programme based on exercise and diet counseling was a effective as insulin treatment in controlling blood glucose ,and prevent the weight gain usually accompanying the introduction of insulin treatment. A study was conducted on short term impact of a brief lifestyle intervention based on yoga on some of the biochemical indication of risk for cardiovascular disease and diabetic. The variables of interest were measured at the beginning (day 1) and end (day 10) of the intervention , using a pre post design qS subject were included in the study (67 males, 31 female ) ages 20-74 years. The Present study includes to assess the knowledge regarding diabetic complication among adults.Keywords
Assess, Diet, Yoga, OHA, Diabetic complication, Adults, Cardiovascular disease and diabeticIntroduction
A study reviewed evidence from literature on life style type 2 diabetics pertinent to physical activity and diet and life style modification to determine the relevance of this evidence to clinical practice. Study result showed that direct evidence supports intervention for physical activity and diet modification for primary prevention and management of type 2 diabetics. It is evidence that supporting patient to make changes in their physical activity and dietary habits can prevention onset of type 2 diabetes and its management translating this findings into effective recommendation for clinical practice. A Study administered structured knowledge, belief and practices regarding diabetes to 199 subjects with diabetic ( 92.5% type 2 diabetic mellitus ) attending the Aga khan university hospital, Karachi. Mean age was 53, mean duration of diabetics was 7 years in men and 6 years in women. Men had a significantly there was no significant difference in the beliefs and practices scores.
A Study to determine and compare the knowledge, beliefs and practice of diabetics receiving free medical care and those paid for medical care in Tamil Nadu. India was undertaken, a questionnaire was administered to elicit diabetic patients with intensive life style intervention was conducted the search revealed 16 published intervention . 8 of which were conducted in the U.S and involved populations disproportionately burdened by diabetes. Eg. (American Indians, native Hawaiians, Mexican American and Africa Americans) the studies reporting results among youth there were post test improvement in intervention groups in knowledge preventive behavior and self-esteem .among studies reporting results among adults, most reported improvement in intervention groups in knowledge or adoption of regular physical activity. Conclusion of the study started that there is a critical need to conduct and published reports on well designed community based diabetes prevention research and share information on the process results and lessons learned , armed with recent positive finding about diabetes prevention and literature documenting community based efforts advocates at local, states and national level can collaborate to stem the rising tide of diabetes in community. A survey to determine the demand for health education among patient by means of evaluating in the level of their knowledge was done . the survey showed that 54% of the subject not able to explain the mechanism of diabetes, while 39.2% of the patient do not know the nature type 2 diabetes .
The survey results indicated the need for the increasing accessibility and intensity of the education activity in diabetes health care. Knowledge regarding diet ,exercise adverse effects , habits and other matters . their beliefs about diabetes and their practice regarding diet , medication and self monitoring of blood glucose results showed a large gap between knowledge and action in both groups • study suggested a need for increased efforts towards patients education regarding diabetes mellitus.Research reported poor metabolic control in type 2 diabetes patient attending a primary care clinic in Trinidad. In an attempt to explain the poor metabolic control.
They studied the primary care patient theoretical knowledge of diabetic control and risk factors. 254 diabetes patient are recruited consecutively although majority of the patients (81%) were the cigarette smoking is a diabetes risk factors , a majority were aware that obesity (66%) physical inactivity (74%) and being a relative of a diabetic patient (79%) constitute diabetes risk factors again the majority of the patient were aware that healthy diet (95%) exercise (95%) and weight loss (87%) are beneficial in diabetes control . while media (49%) was the commonest sources of diabetes information, doctors and nurses were consulted by (4O%)and (11%) of patient respectively, study suggested the need Sor immense health education in the community regarding the risk factors of diabetes.A literature review of community based intervention intended to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes, based on recently .published finding about the potential to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Materials and Methods
This describes methodology to assess the knowledge regarding diabetic complication among men (30- 60) years at Hindu mission hospital. It consists of research approach, research design, setting of the study, population, sample, sampling techniques and sample selections criteria.
Research approach
Quantitative research used in this study.
Research design
Descriptive design is adapted for the study.
Settings of the study: The study was conducted in guduvancherry with comprises of total population of 60000 it is about 10 km from Hindu Mission School of Nursing
Population
The samples consisted of all women residing at Guduvancherry
Sample
The study population comprised of women between the age group of 20-45 years living in Guduvancherry.
Sample size
The sample size was 50 mothers.
Sampling techniques
A non-probability purposive sampling technique is adopted to Select the samples in the study.
Description of the tools
The tools consist of 2 sections
Section 1
It consists of on interview schedule to demographic characteristics such as age religion educational status family income, marital status. occupation and source of information.
Section 2
Multiple choice question to assess the knowledge on diabetic complications.
Criteria for scoring
Section 1; no scoring
SECTION 2;
The knowledge questionnaire consisted of 10 questionnaire totally , each question with correct answers carries one mark and wrong answers carries no mark, the total scoring for over all knowledge is 10. Interpret the level of knowledge of diabetic complication, the scores converted and classified as follows.
Adequate; 7&_100%
Moderately adequate; 51% „75%
Inadequate; <50%
The data was collected Erotti 30 members and analyzed according to the objectives of the study . The chapter deals with interpretation and includes descriptive statistics. The finding of the study were organized and presented
Results
Assessment of knowledge regarding diabetic complication.
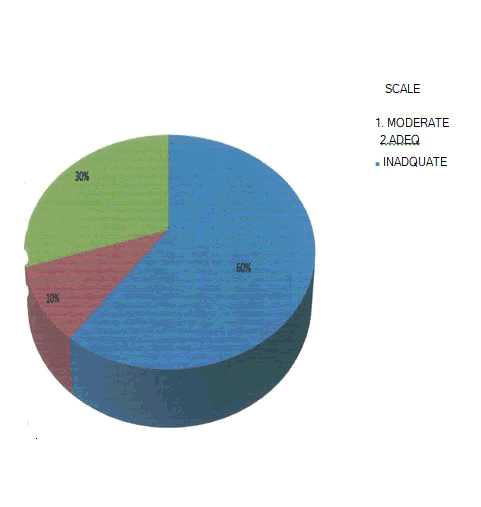
Diabetes Complication regarding knowledge 30% of them having adequate knowledge, 1O% of them having moderately adequate knowledge and 60% of them having in adequate.
Figure 1: Distribution of level of knowledge regaring.
To assess the level of knoeledge regarding diabetic mellitus
1) Which part of body will affect due to diabetic mellitus?
66% of them got knowledge of kidney, heart, eye, brain and nerves , 30% of them got knowledge of skin, 4% of the got knowledge dental.
2) What may be the symptoms of diabetic mellitus due to kidney dysfunction?
63% of them got knowledge of polyurea , 23% of them got knowledge of olyurea, 14% of them got knowledge of abdomen pain.
3) What may be the symptoms of diabetic mellitus due to heart dysfunction?
36 % of them got knowledge of giddiness , 60% of of heart attact , 4% of them were knowledge of I don’t know.
4) What may be symptoms of diabetic mellitus due to brain dysfunction?
36% of them got knowledge of paralysis, 40% of them get knowledge of headache , 24% of them get
knowledge of I dontknow.
5) What may be the symptoms of diabetes mellitus due to eye dysfunction?
70% of them got knowledge of blindness 14% of them get knowledge of diarrhea , 16% of them get knowledge of sleeping.
6) What is the signs and symptoms of increased glucose level in the blood?
74% of the got knowledge of giddiness , 26% of them got knowledge of sleeping, 0% of them got knowledge of diarrhea,
7) How often the wound get healed due to diabetic mellitus?
34% of them got knowledge of healing , 40% of them got knowledge of not healing ,26% of them got knowledge of spread wound.
8) What are the food sources can take in case of diabetic mellitus?
100% of them got knowledge of increased water content in food idem , 0% of them got knowledge of increased cholesterol diet , 0% of them got knowledge of increased salt diet.
9) What is the causes of diabetic complication?
34% of then got knowledge of improper diet, 26% of them got knowledge of irregular medicine, 40% of them got knowledge of all the above.
10) How many years of treatment need for the diabetic mellitus patients?
36% of them got them got knowledge of knowledge of life long... knowledge of 6 months,14% of one years ,50% of them got knowledge of all the above.
Conclusion
The findings of this study regarding knowledge 30% of them having adequate knowledge ,10% of them having moderately adequate knowledge and 60% of them having in adequate knowledge.
Summary, Implication
Summary
The locus of the study was to assess the effectiveness of structured teaching programme on knowledge regarding diabetic complication among adult at Tambaram.
Objective of the study: To assess the knowledge regarding diabetic complication among adults.
Nursing implications
The investigation has drawn following implication from the study which is vital concern for Nursing services, nursing administration and nursing research.
Nursing practice: The medical health nurse plays a vital role in educating and motivating people for knowledge regarding diabetic complication. Health education can be provided through mass health education Programme through the clients to increase awareness and knowledge on diabetic complication. In services education can be important to staff working in a medical in order to make awareness about diabetic complication.
Nursing education: The medical health nurse has an educator to incorporate the major study finding in nursing curriculum at all in order to equip the students.
Nursing administration:The medical health nurse administration should collaborate with governing bodies to create policies in order to awareness regarding diabetic complication. Nurse administrator along with governing bodies formulate programme to focus on diabetic complication. The administrator should take initiative in arranging awareness program they should involve in distributing health educating materials like flash card, pamphlets, leaflets etc, the study should create awareness regarding complication of diabetic mellitus through information booklets.
Nursing reseaech: The finding of the study can be disseminated to Medical health nurse. Nurse practitioner and the student nurse through internet journals etc..., the finding of the study will help the professional nurse and nursing to gain the knowledge regarding complication of diabetic mellitus.
Funding
No funding sources.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Conflict Of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The encouragement and support from University, Chennai, India is gratefully acknowledged for providing the laboratory facilities to carry out the research work.
References
- Bundhamcharoen, Kanitta, Odton Patarapan, Phulkerd Sirinya, and Tangcharoensathien Viroj. "Burden of disease in Thailand: changes in health gap between 1999 and 2004." BMC Pub Healt 11, (2011): 1-9
- Vélez, Maria P, Connolly Michelle P, Kadoch IJ, and Phillips S, et al. "Universal coverage of IVF pays off." Hum Repro 29, (2014): 1313-1319.
- Aekplakorn, Wichai. "Prevalence, treatment, and control of metabolic risk factors by BMI status in Thai adults: National Health Examination Survey III." Asia Pac J Pub Heal 23, (2011): 298-306.
- Lamster, Ira B, Lalla Evanthia, Borgnakke Wenche S, and Taylor George W. "The relationship between oral health and diabetes mellitus." J Amer Dent Assoc 139 (2008): 19S-24S.
- Taylor, Georg W, and Borgnakke Wenche S. "Periodontal disease: associations with diabetes, glycemic control and complications." Or Dise 14, (2008): 191-203.
Author Info
Department of Nursing, Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Selaiyur, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, IndiaCitation: Muthupriya, AR. Bharathi Assessment of Knowledge Regarding Diabetic Complication among Adults , J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(11): 1-4
Received: 01-Dec-2021 Accepted: 15-Dec-2021 Published: 22-Dec-2021