Commentary Article - (2021) Volume 9, Issue 12
An Analytic Study of Colonic Malignancy in Our Institution
Essam H. Dhandapani and A. Jayakrishna Reddy*
*Correspondence: A. Jayakrishna Reddy, Department of General Surgery, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, Email:
Abstract
Colorectal malignancy is the second most commonly reported cancer world wide. Colon cancer is reported to be very common among women and rectal among females. Though chemo and radiation therapy is given for these colonic malignancy, surgery becomes the only ϐinl choice. Hence this study aims to determine the incidence of age, sex, common clinical manifestations of the malignancies, pathological evaluation and morbidity and mortality associated with types of colonic tumours. Methodology: The patients (45 No’s) who were conϐimed histologically with colonic malignancy were taken up for the study. Blood biochemistry assessments including LFT to assess general conditions, Colonoscopy to conϐim the location and nature of the growth, USG abdomen to image the liver to check for secondary deposits were diagnosed on the samples. From the study samples, of the total 35 patients, males constituted 21 patients (60%) and females constituted 14 patients (40%). The frequency of distribution of malignancy is depicted.
Description
Colorectal malignancy is the second most commonly reported cancer world wide. Colon cancer is reported to be very common among women and rectal among females. Though chemo and radiation therapy is given for these colonic malignancy, surgery becomes the only final choice. Hence this study aims to determine the incidence of age, sex, common clinical manifestations of the malignancies, pathological evaluation and morbidity and mortality associated with types of colonic tumours.
Table1: Frequency of distribution.
| Site | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Caecum | 7 | 0.21 |
| Ascending Colon | 6 | 0.2 |
| Hepatic Flexure | 3 | 0.0857 |
| Transverse Colon | 1 | 0.0225 |
| Splenic Flexure | 1 | 0.0225 |
| Descending Colon | 5 | 0.125 |
| Sigmoid & Recto sigmoid | 12 | 0.342 |
For right-sided tumors commonest clinical manifestation is pain abdomen which presents with intermittent colic in 68% of patients due to the mass impinging the lumen of the colon and for left sided tumors, altered bowel habits is the commonest manifestation, presenting with intermittent diarrhoea and passing mucus in 60% of patients.
Mass abdomen as a clinical manifestation were seen in 58% of patients with right sided tumors and in 13% of patients with left sided tumor. Only 3 patients 13%with left sided tumors both are with sigmoid carcinoma presented with acute obstructive features. Clinical manifestation with only constitutional symptoms of fever,
Methodology: The patients (45 No’s) who were confirmed histologically with colonic malignancy were taken up for the study.
Blood biochemistry assessments including LFT to assess general conditions, Colonoscopy to confirm the location and nature of the growth, USG abdomen to image the liver to check for secondary deposits were diagnosed on the samples.
From the study samples, of the total 35 patients, males constituted 21 patients (60%) and females constituted 14 patients (40%).
The frequency of distribution of malignancy is depicted in table 1.
anaemia and weight loss occurred in two patients were16% with right sided tumors. Pain abdomen as a feature occurred in13% of patients with left sided tumors. Out of the total 35 cases , the following is the frequency of each macroscopic appearance of colonic tumors. The most common stage at presentation is stage IIIa accounting for 42.8% of cases.
Nodal metastases are present in 74%.Hepatic metastases are present in 7.5% of cases. One patient died in postoperative period after re-laparotomy for anastomotic leak. One emergency laparotomy patient died postoperative period due to his stage IV disease and general condition.
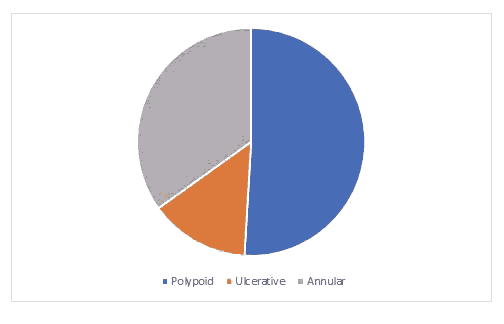
Figure 1: Colonoscopy.
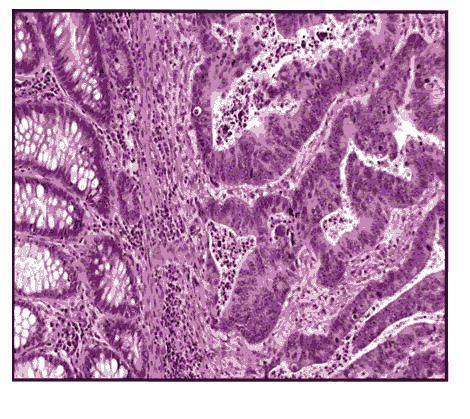
Figure 2: Histopathology of moderate to poorly differentiated samples.
References
- Skibba, Richard M, Gourley William K, and Klotz Arthur P. "Early detection and prevention of colon cancer: The role of colonoscopy." Arch inte med 136, (1976): 890-892.
- Sabiston, David C, Townsend Courtney M, Beauchamp R D, and Evers BM, et al. Sabiston textbook of surgery: the biological basis of modern surgical practice. Wb Saunders, 2001.
- Borda, F, Frauca A, Martínez-Peñuela JM, and Sánchez MF, et al. "Endoscopic polypectomy in malignant colorectal adenoma. Review of our cases and therapeutic considerations." Rev Esp las Enfermedades Apar Digestiv 74, (1988): 339-342.
- Weiss, L, Grundmann E, Torhorst J, and Hartveit F, et al. "Haematogenous metastastic patterns in colonic carcinoma: an analysis of 1541 necropsies." J Path 150, (1986): 195-203.
- Hughes, Kevin S. "Resection of the liver for colorectal carcinoma metastases: a multi-institutional study of indications for resection." Surgery (1988).
Author Info
Essam H. Dhandapani and A. Jayakrishna Reddy*
Department of General Surgery, Sree Balaji Medical College & Hospital Affiliated to Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, IndiaCitation: Essam H. Dhandapani, A. Jayakrishna Reddy An Analytic Study of Colonic Malignancy in Our Institution, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2021, 9(11): 1-2
Received: 01-Dec-2021 Accepted: 15-Dec-2021 Published: 22-Dec-2021
