Case Report - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 11
A Case of Post Traumatic Left Hand 4th Proximal Phalanx Fracture with Lacerated Wound over 4th Digit
Pratik Mahapatra, Vijay Narasimman Reddy* and Mervinrosario
*Correspondence: Dr. Vijay Narasimman Reddy, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Balaji Medical College, Chromepet, Chennai, Tamilnadu, India, Email:
Abstract
Introduction: Phalanges fractures are common and more than half of these are work related. They may be caused by direct injury causing swelling or open injury. Improper treatment may cause stiff finger.
Case report: A 42-year-old female came to the casualty with complain of pain in her left hand and laceration over her
4
Conclusion: Traumatic phalanges fracture when treated judiciously can give a good functional outcome.
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Haberler
Keywords
Phalanges fractures, Wrist and forearm, Proximal phalanx transverse, Shaft fracture
Introduction
Proximal phalanx fractures result from high energy trauma sustained to hand. Proximal phalanx fractures usually angulate into extension. The proximal fragment goes into extension due to interossei and the distal fragment goes to extension. Industrial or other environmental settings sometimes lead to crushing mechanism due to bending, shearing and torsion causing fracture and soft tissue damage [1-3].
Case Presentation
A 42 years housewife was brought to the Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital casualty by her family members who gave a history of alleged fall from bike. After which she had pain over her left hand. The patient was conscious and oriented with no history of loss of consciousness or any episode of vomiting. Physical examination revealed a lacerated wound over her 4th digit with generalised swelling over her hand with reduced range of motion. She had no tenderness over her metacarpals or wrist joint. Her medical, surgical, allergy history was unremarkable (Figures 1 and 2) [4-6].
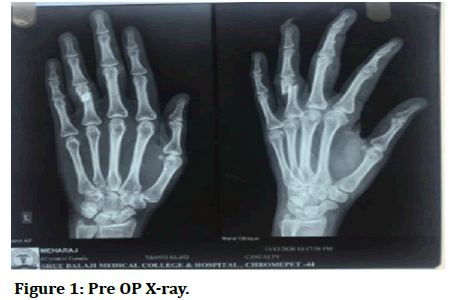
Figure 1: Pre OP X-ray.
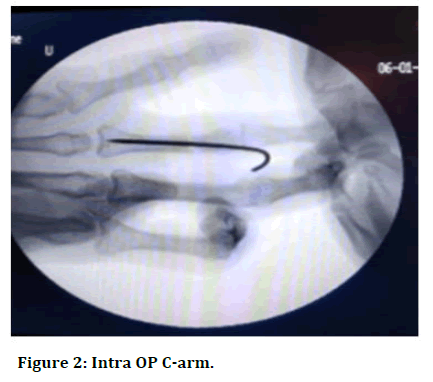
Figure 2: Intra OP C-arm.
The x-ray of her left hand in AP and oblique view revealed a 4th proximal phalanx transverse fracture. The patient was explained about the condition, surgical procedure, and prognosis. The patient consented for the surgery. Before the day of surgery patient was asked to be on nil per oral. On the day of surgery patient was shifted to pre OP and after assessment by anaesthetist was shifted to the OT where she was given regional block by the anaesthetist. After which patients hand was put on arm board and parts prepared and draped. Fracture was visualised under C arm and K wire was passed from middle interphalangeal joint towards the proximal interphalangeal joint. Reduction was found satisfactory and then the remaining length of k wire was cut and bent. Sterile dressing was then done and patient was put on an above elbow POP. Post operatively patient regained sensory and motor function after 8-10 hours of surgery. Patient stayed in the ward for 2 weeks in which her regular dressing was done and along with it she received regular antibiotics, analgesics and physical therapy. On discharge her condition was stable (Figures 3 and 4).
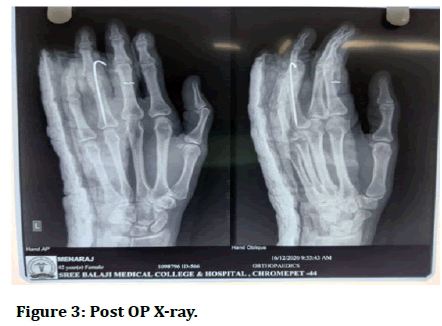
Figure 3: Post OP X-ray.
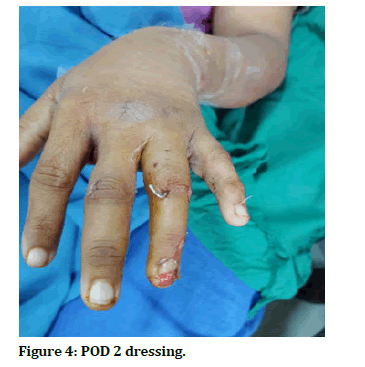
Figure 4: POD 2 dressing.
Discussion
Reduction of displaced fracture is highly essential. When the MCP joint is flexed it is important to check the position of finger and also nail to be in same plane. It depends on type of fracture, simple fracture can be held with splint. If fracture is unstable or reduction is not achieved then surgery is chosen. K wires are less invasive and are perfect for some fractures; also lag screw and plate fixation can be chosen if fracture is spiral, distal condylar etc. Exfix can be used for comminute fracture [6-10].
Conclusion
Proximal phalanx fracture usually results from direct violence or high degree of variation in mechanism of injury. When treated at the proper time without negligence results in better functional outcome for the patient.
References
- Blom A, Warwick D, Whitehouse M. Apley and Solomon’s system of orthopaedics and trauma. 10th Edition, CRC Press, 2018.
- Egol K, Koval KJ, Zuckerman J. Handbook of fractures. 6th Edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2019.
- Weinstein SL, Buckwalter JA. Turek’s Orthopaedics: Principles and their applications. 6th Edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2005.
- Blomberg J, Ahn L. Ortho Bullets, Phalanx fractures. 2022.
- Singh J, Jain K, Mruthyunjaya, et al. Outcome of closed proximal phalangeal fractures of the hand. Indian J Orthop 2011; 45:432-438.
- Carpenter S, Rohde RS. Treatment of phalangeal fractures. Hand Clin 2013; 29:519-534.
- Jones WR. Fractures and joint injuries of the hand. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009; 650-695.
[Indexed]
- Gupta R, Singh R, Siwach R, et al. Evaluation of surgical stabilization of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures of hand. Indian J Orthop 2007; 41:224-229.
- Singh J, Jain K, Mruthyunjaya, et al. Outcome of closed proximal phalangeal fractures of the hand. Indian J Orthop 2011; 45:432-438.
- Horchbach EE, Cohen MS. Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning of fractures of the proximal phalanx. J Hand Surg Br 2001; 26:45-49.
Author Info
Pratik Mahapatra, Vijay Narasimman Reddy* and Mervinrosario
Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Balaji Medical College, Chromepet, Chennai, Tamilnadu, IndiaCitation: Pratik Mahapatra, Vijay Narasimman Reddy, Mervinrosario, A Case of Post Traumatic Left Hand 4th Proximal Phalanx Fracture with Lacerated Wound over 4th Digit, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2022, 10 (11): 058-059.
Received: 02-Sep-2022, Manuscript No. JRMDS-22-57341; , Pre QC No. JRMDS-22-57341(PQ); Editor assigned: 06-Sep-2022, Pre QC No. JRMDS-22-57341(PQ); Reviewed: 21-Sep-2022, QC No. JRMDS-22-57341; Revised: 03-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. JRMDS-22-57341(R); Published: 10-Nov-2022
